Welcome to the monthly SHDA Research Update. Our specialists have selected 3 seminal papers that have been recently published in each speciality (Cardiology, Cardiac Surgery, Cardiac Imaging, Perioperative Medicine).
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
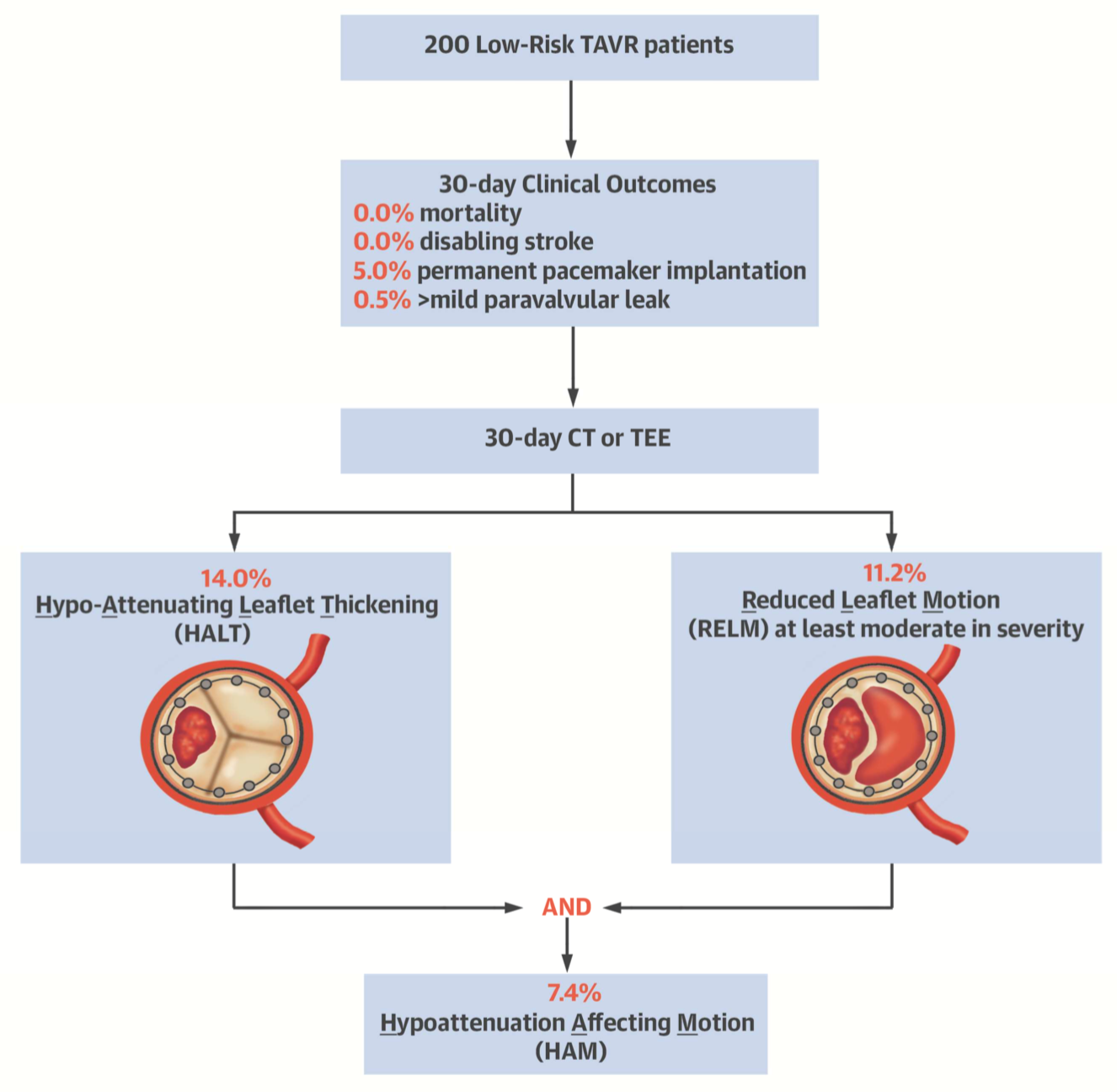
The benefits of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) are progressively being explored in lower risk patients. This multi-centre study evaluated 200 low-risk patients with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis, comparing to historical controls who underwent surgical AVR. Overall 30 day outcomes were good, with shorter mean length of stay (2.0±1.1 days), zero mortality, zero disabling stroke, lower rates of post-operative AF, and low procedural complication rates. Rate of pacemaker insertion was comparable, and 14% of TAVR patients had evidence of subclinical leaflet thrombosis.
Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD) and its antecedent acute rheumatic fever remain prevalent in many third world countries, and in disadvantaged communities of wealthy nations. After a period of relative neglect, this preventable disease is again gathering community attention. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, epidemiology and impact of RHD worldwide, with a special focus on health policy and prevention.
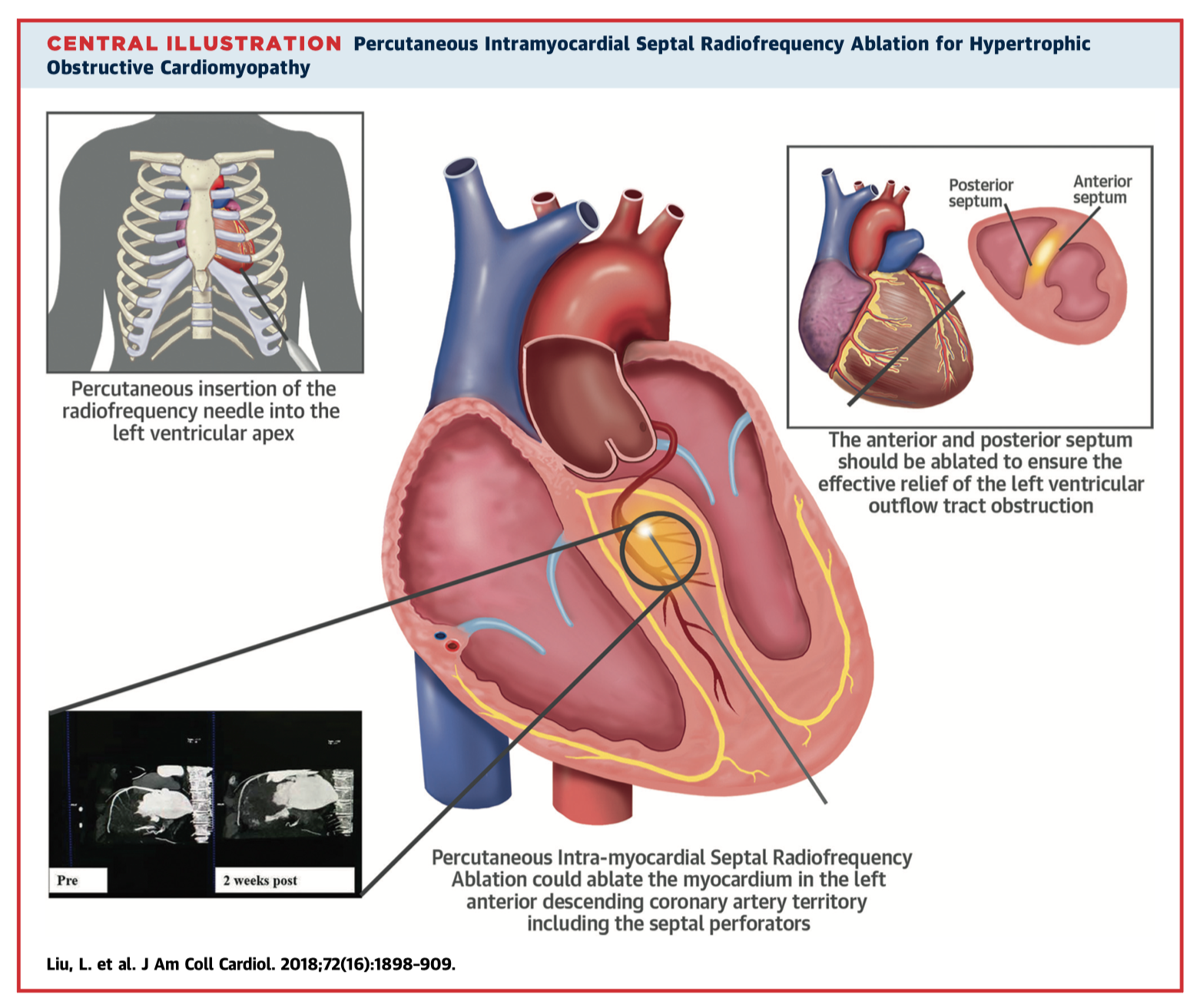
Echocardiography-guided percutaneous intramyocardial septal radiofrequency ablation (PIMSRA) is shown here to be an effective, minimally-invasive therapy in 15 patients with symptomatic hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM). The procedure significantly reduced peak left ventricular outflow tract gradient both at rest and under stress, significantly reduced interventricular septal thickness, with corresponding improvement in symptoms (NYHA class 3 to class 1, p<0.0001), and biochemical markers at 6 months (median pro-BNP 924 pg/ml to 137 pg/ml, p=0.028).
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
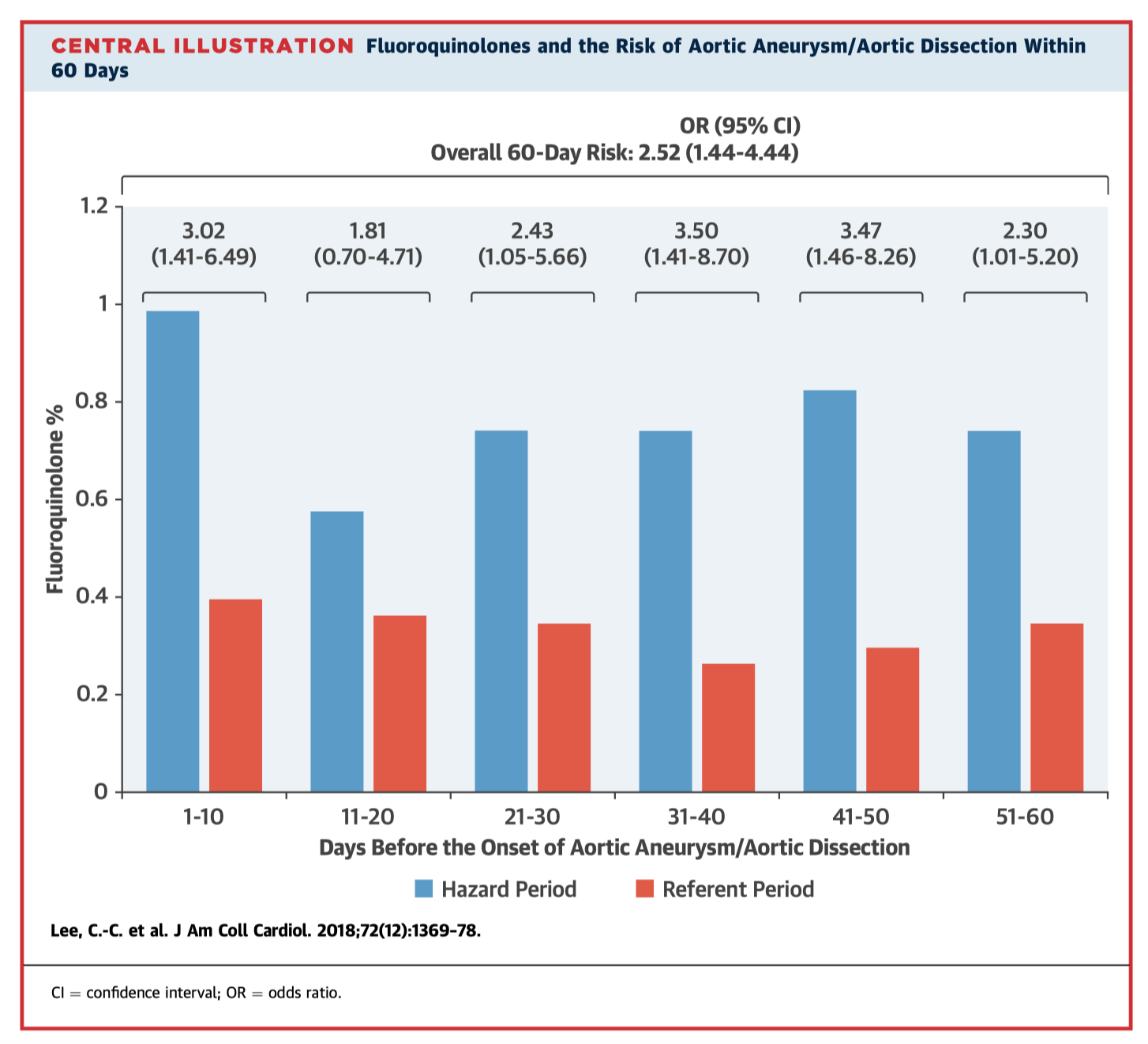
This case-crossover analysis evaluated the association between fluoroquinolone treatment and serious collagen disorders, aortic aneurysm and dissection (AA/AD). 1,213 hospitalised AA/AD patients were identified between 2001 and 2011. In the main analysis, exposure to fluoroquinolone was more frequent during the hazard periods than during the referent periods (1.6% vs. 0.6%; OR 2.71). An increased risk of AA/AD was observed for prolonged exposure to fluoroquinolones (OR 2.41 for 3-14 day exposures, OR 2.83 for >14 days). The authors concluded that exposure to fluoroquinolone was substantially associated with AA/AD, with risk modifiable by the duration of fluoroquinolone use and the length of the hazard period.
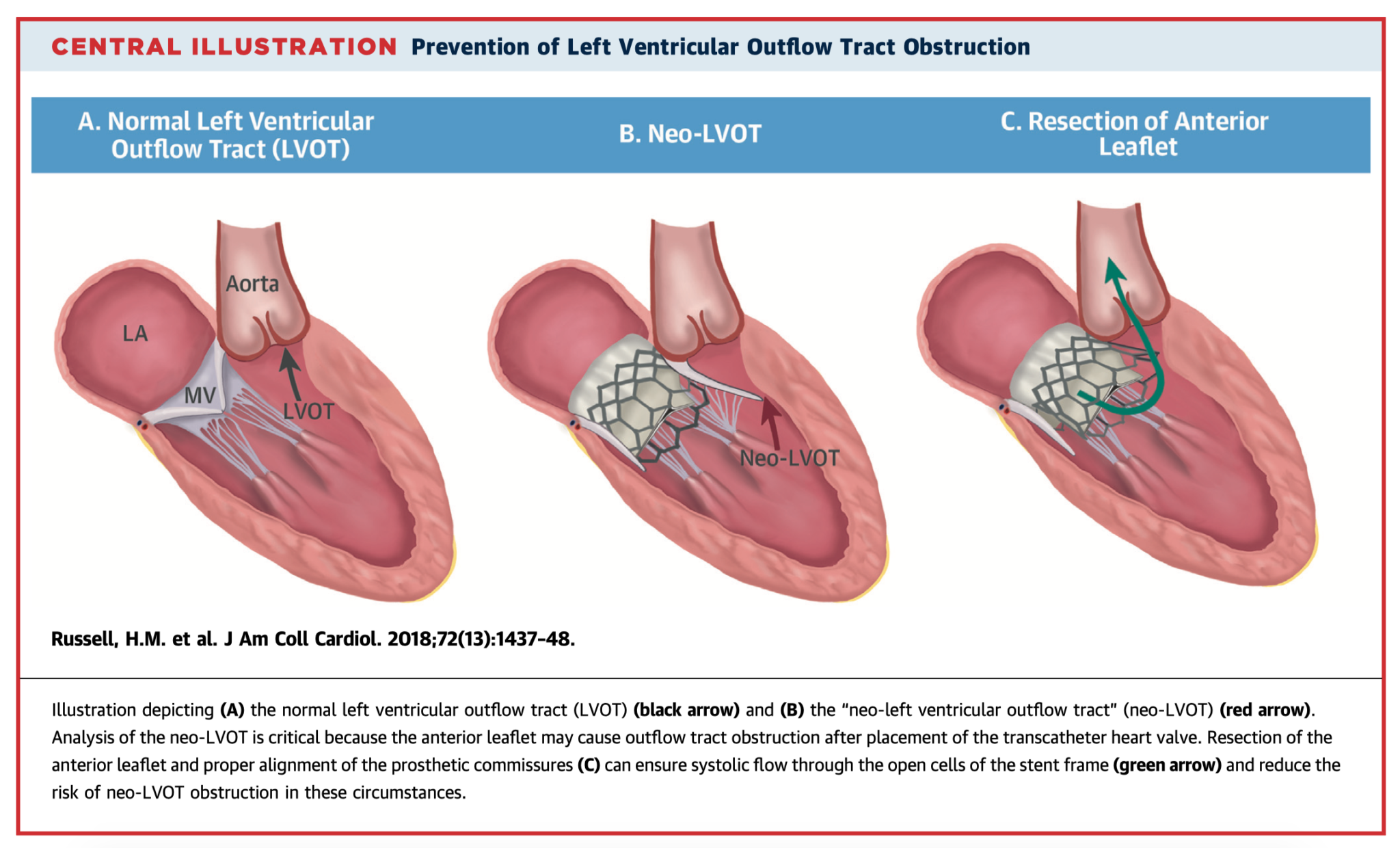
The authors have described step-by-step a novel technique for insertion of a balloon-expandable aortic transcatheter heart valve in patients with mitral annular calcification. Pre-procedural planning, surgical techniques and variations are described in detail. Eight patients underwent this procedure. Technical success criteria was 100%, with zero in-hospital and 30-day mortality. The authors concluded that this technique is reproducible and useful in treating patients with severe MAC.
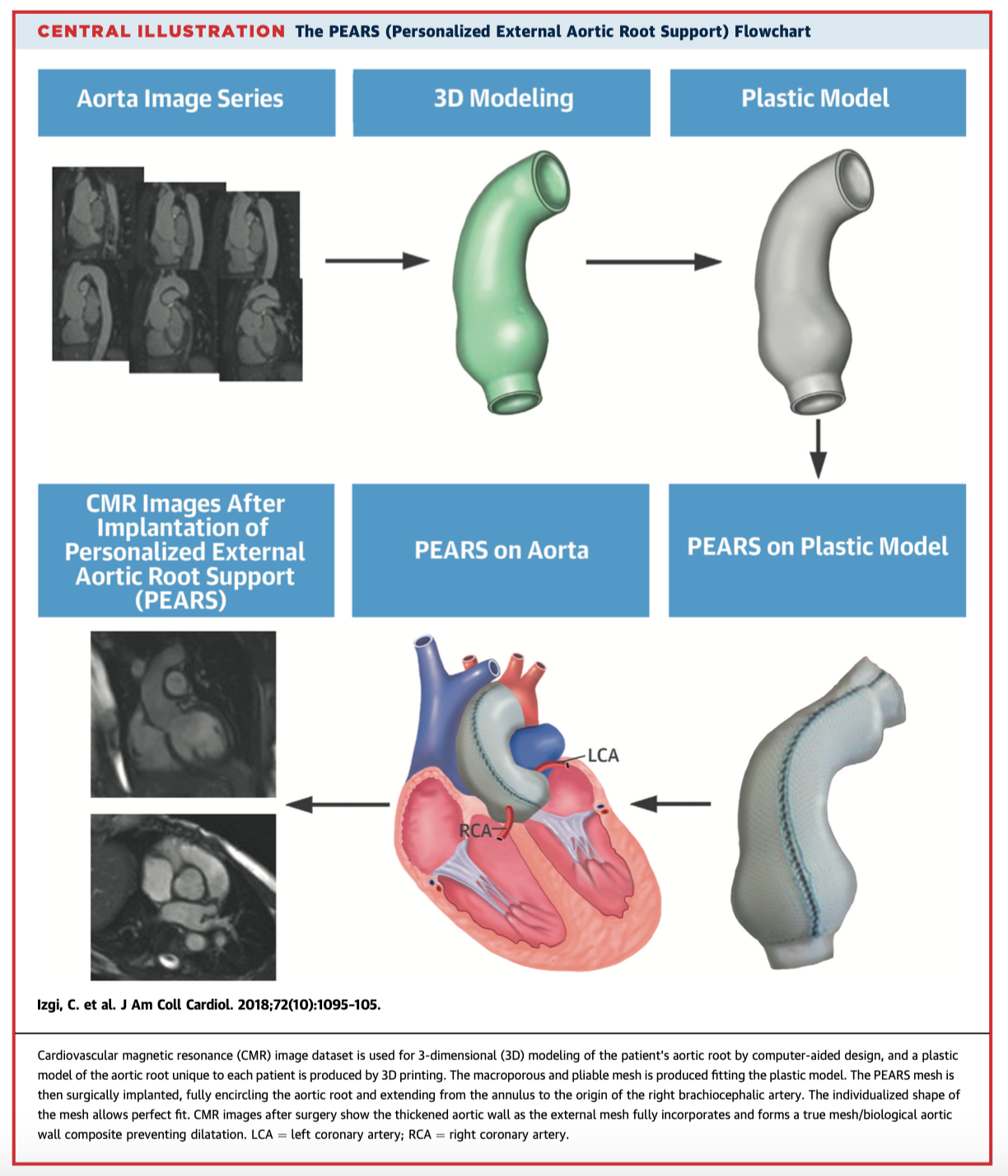
Personalised external aortic root support (PEARS) was introduced in 2004 for prevention of aortic root dilatation. This study assessed the effectiveness of PEARS in 24 patients with Marfan syndrome. There was no increase in the aortic root and ascending aorta diameters, but there was a tendency toward reduction: annulus diameter 28.9 +/- 2.3 mm to 28.5 +/- 2.4 mm (change – 0.39 mm), sinus of Valsalva diameter 44.9 +/- 2.9 mm to 44.5 +/- 3.0 mm (change – 0.37 mm), and ascending aorta diameter 32.4 +/- 3.6 mm to 32.3 +/- 3.7 mm (change – 0.10 mm,). The authors concluded it is a viable alternative to aortic replacement for prevention of dissection in Marfan patients.
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
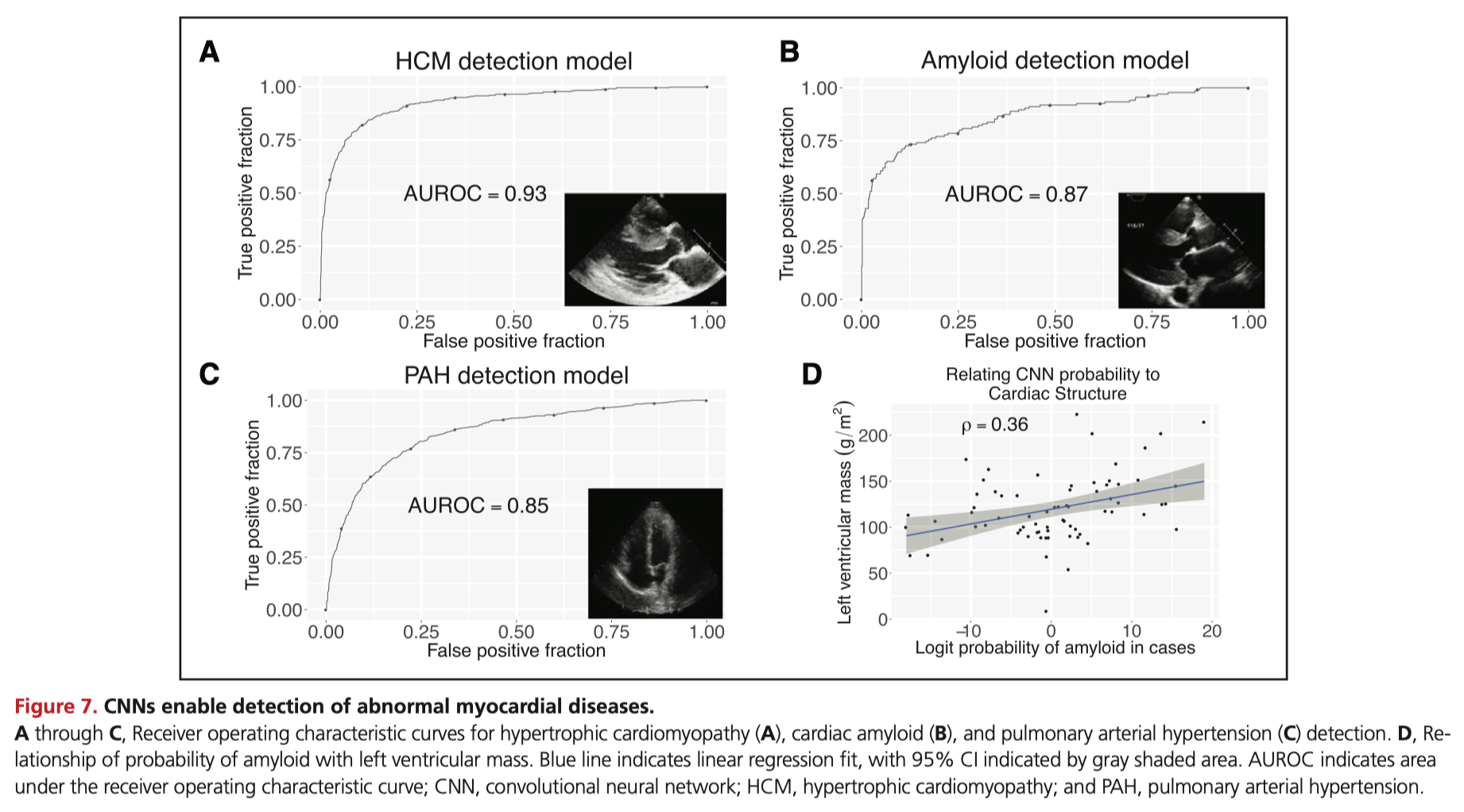
Echocardiography is a mainstay of diagnosis and management, but barriers remain high, chiefly driven by the expertise required in image acquisition and interpretation. This paper by Zhang et al. is a true attempt to democratise and revolutionise the use of echocardiography by breaking down such barriers. Using neural networks and a database of 8666 echocardiograms, models were developed for automated identification of common viewpoints, chambers, and echocardiographic parameters. Overall, the model had good concordance with reported values, and three models for disease identification had good accuracy (C statistic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 0.93, pulmonary arterial hypertension 0.85, and cardiac amyloid .87). The author’s prove the automated scalability of the model, analysing 14000 echocardiograms within 3 weeks for this paper.
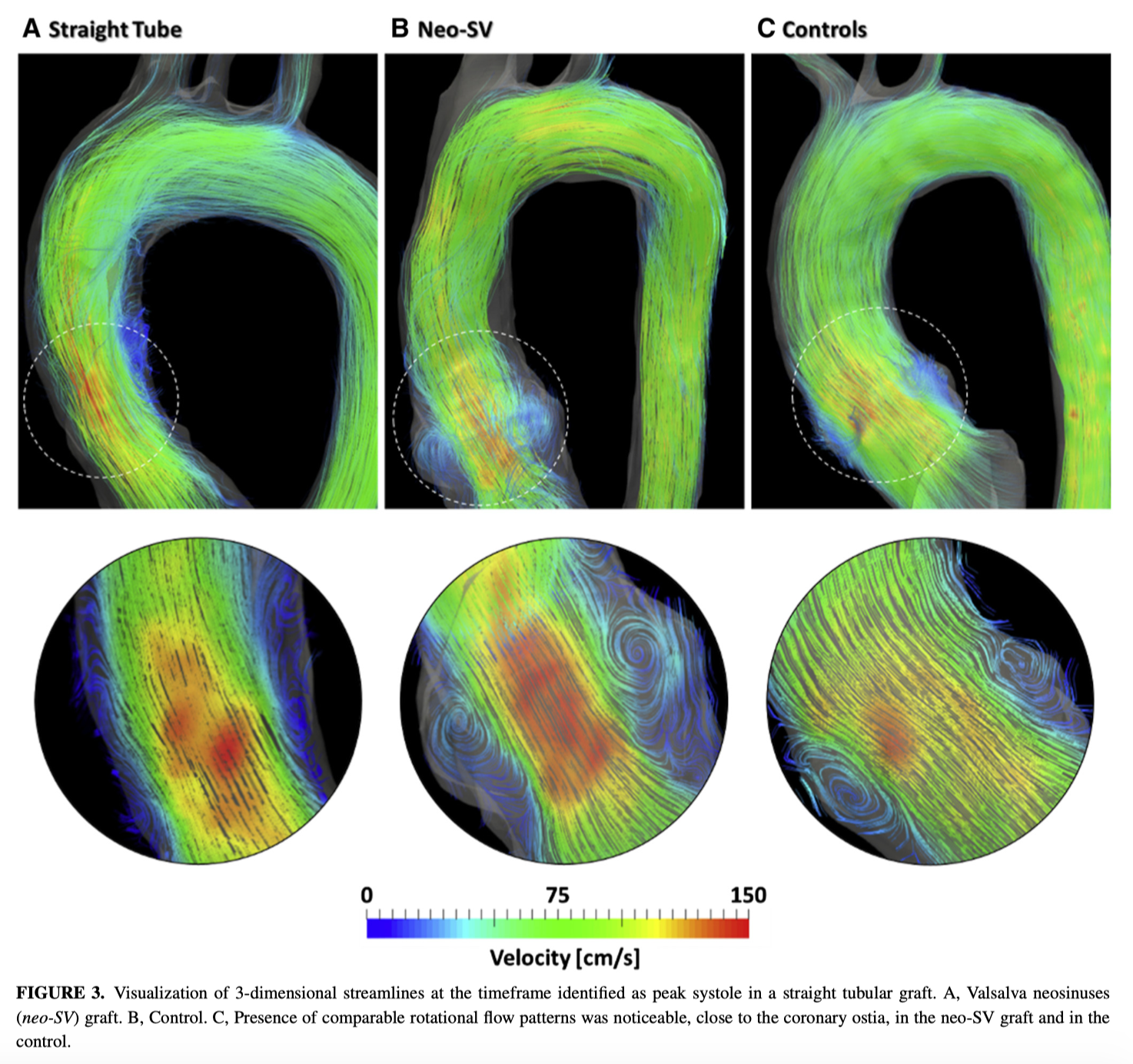
Comparing two aortic root replacement prostheses (straight tube graft vs. prosthesis with recreated Valsalva neosinuses) to matched controls in a total of 30 patients (n=10, 10, 10), there was more physiologic velocities, vorticity and trajectories in those who received the graft with re-created neosinuses of Valsalva. On 4D-flow magnetic resonance imaging, there was significantly lower wall shear stress and lower velocity compared to the tube graft. The author’s hypothesise long-term benefits on distal aortic remodelling and potential to reduce aneurysm formation.
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
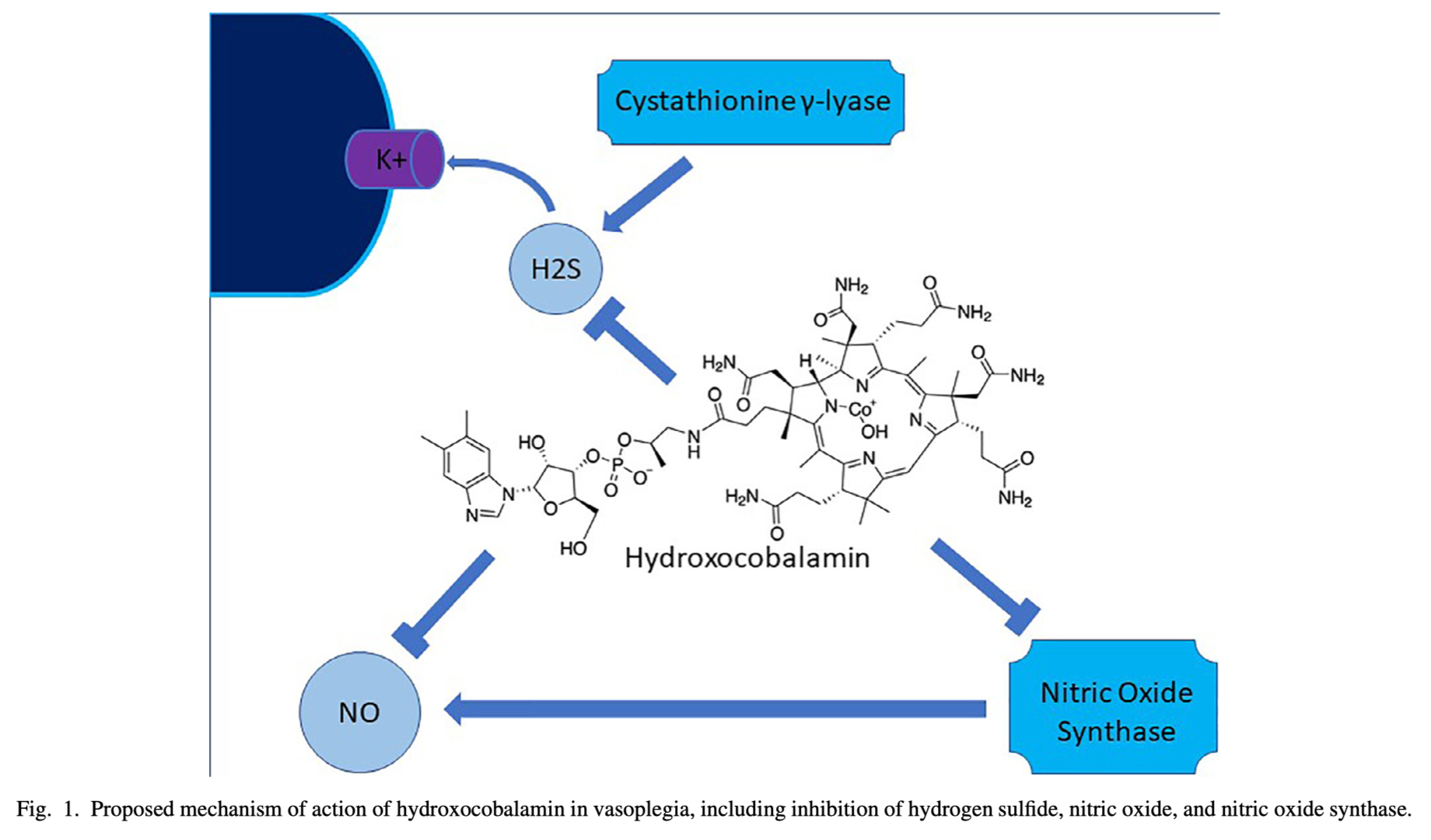
Cobalamins, including hydroxocobalamin, are potent direct inhibitors and binders of NO and likely function as direct inhibitors of NO synthase. Thus, hydroxocobalamin seems to have a dual effect on the NO-mediated component of vasoplegia. Side effects may include chromaturia, erythema, hypertension, acneiform rash, headache and photosensitivity. In this article the authors have reviewed the use of hydroxocobalamin as rescue therapy in patients with severe vasoplegia, however there are a lack of high-quality, randomized, controlled data regarding efficacy.
This retrospective single centre study of 19 patients studied the utility of levosimendan and vasopressin for new onset acute pulmonary hypertension after weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass. In theory levosimendan provides inotropic support of the right ventricle in conjunction with a vasodilatory effect on the pulmonary circulation. This is combined with vasopressin and norepinephrine to maintain systemic mean arterial pressures. Mean pulmonary artery pressure decreased from 32 +/- 9 to 26+/- 6 mmHg (p=0.039) in the first 24 hours along with an increase in cardiac output (3.2 +/- 1 to 4.2 +/- 1.1 L/min; p = 0.012) and resolution of lactic acidosis. The authors concluded it may be an effective treatment.
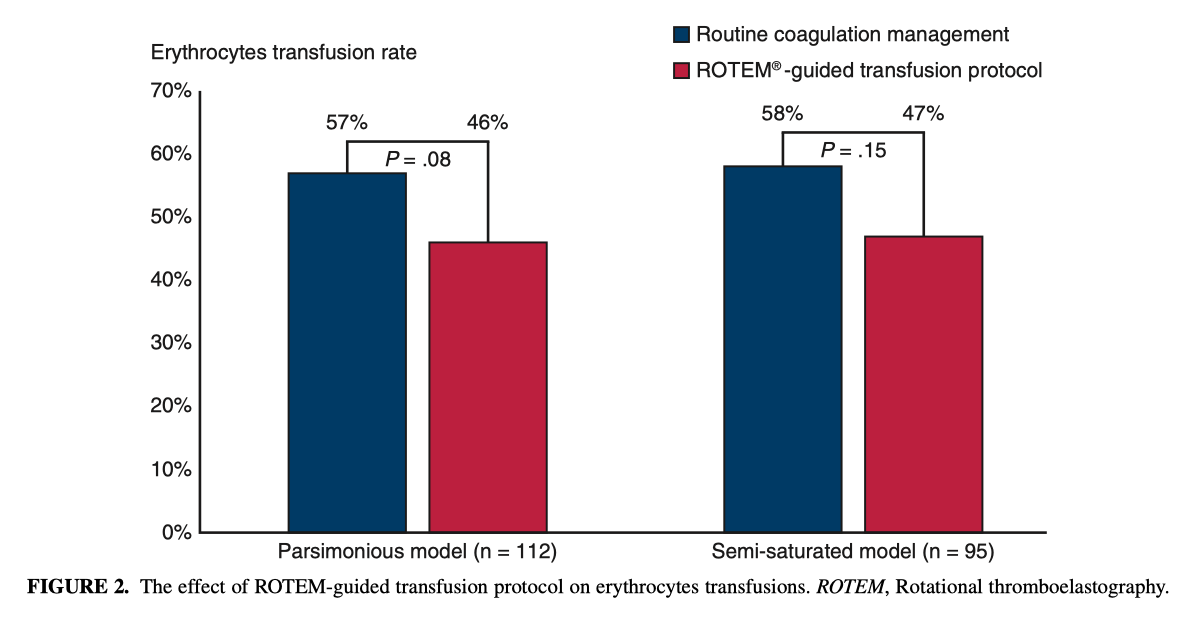
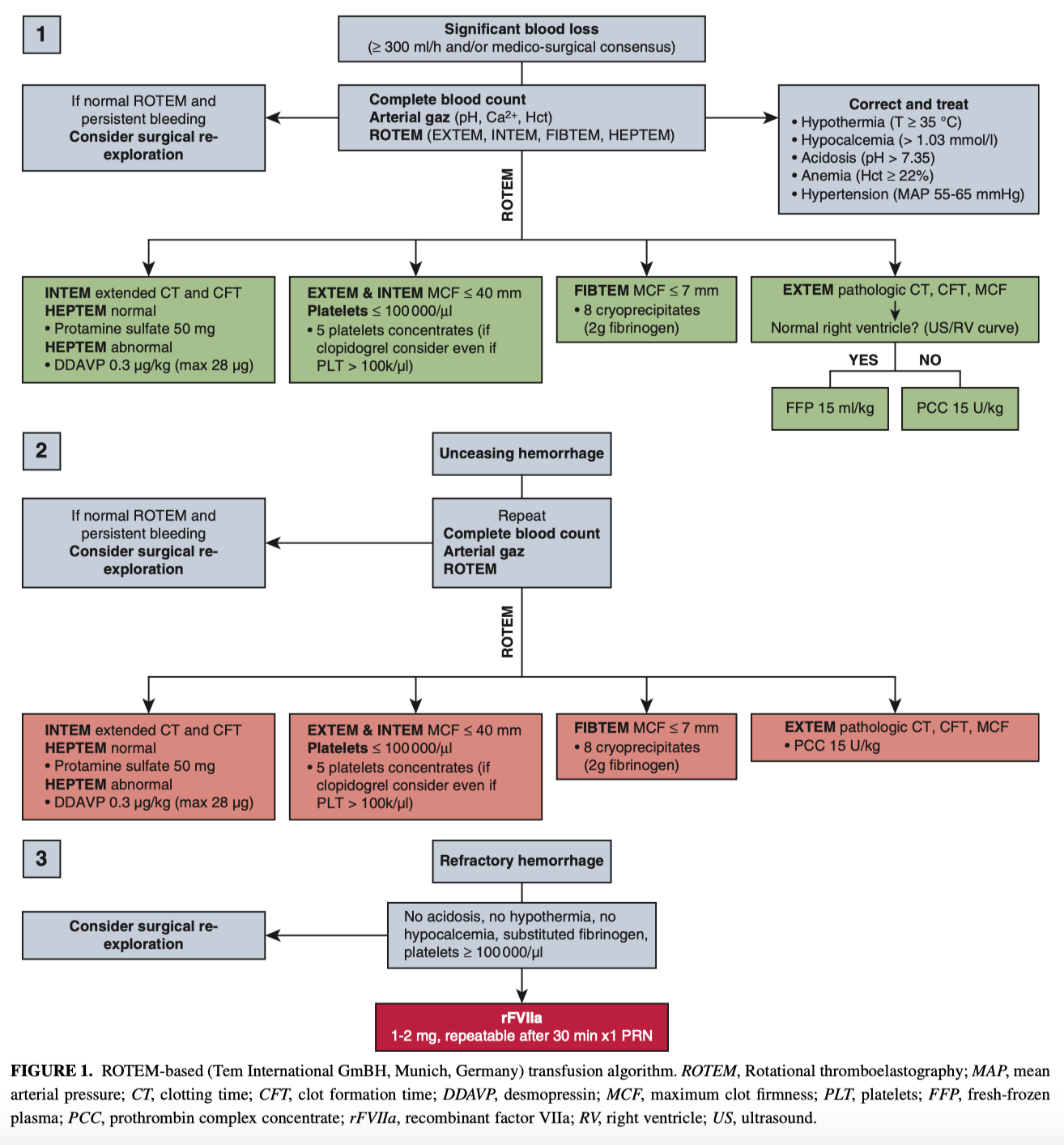
This single-center retrospective analysis based on 385 consecutive patients undergoing surgery involving the aortic root, ascending aorta, or aortic arch compared 197 controls managed according to routine transfusion protocol before the introduction of the ROTEM in 2012 with 188 patients operated afterward. ROTEM implementation was associated with a trend toward reduction in the rate of erythrocytes transfusion (57% vs 46%, p=.08) and a decreased median number of units transfused for erythrocytes (1.0 [0.0-4.0] unit vs 0.0 [0.0-2.0] unit, p=.03) and plasma (0.0 [0.0-4.0] unit vs 0.0 [0.0-2.0] unit, p=.04). After sensitivity analysis, ROTEM displayed a comparable rate of erythrocytes transfusion (58% vs 47%, p=.15). The authors concluded that in a real world setting, ROTEM-based algorithm implementation could help reduce excess erythrocyte transfusion for complex aortic procedures.