Welcome to the monthly SHDA Research Update. Our specialists have selected 3 seminal papers that have been recently published in each speciality (Cardiology, Cardiac Surgery, Cardiac Imaging, Perioperative Medicine).
Cardiology
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
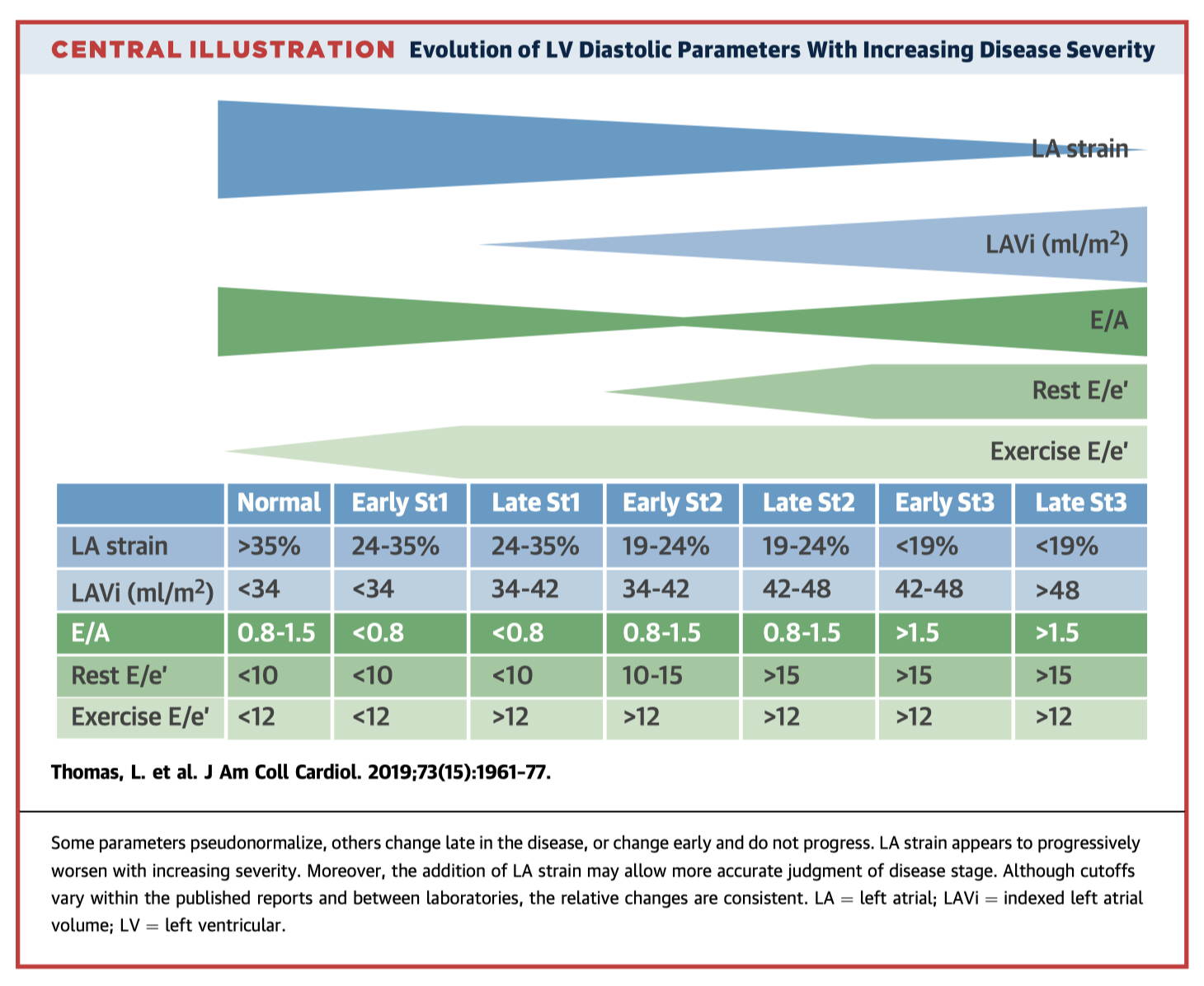
Evaluation of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) remains challenging. There is improving understanding of left atrial (LA) – left ventricular interactions during the cardiac cycle. This paper discusses LA parameters which can improve both the diagnostic accuracy and prognostic value of HFpEF and LVDD diagnostic algorithms. In particular, worsening LA strain appears to correlate with increasing disease severity (see Central Illustration).
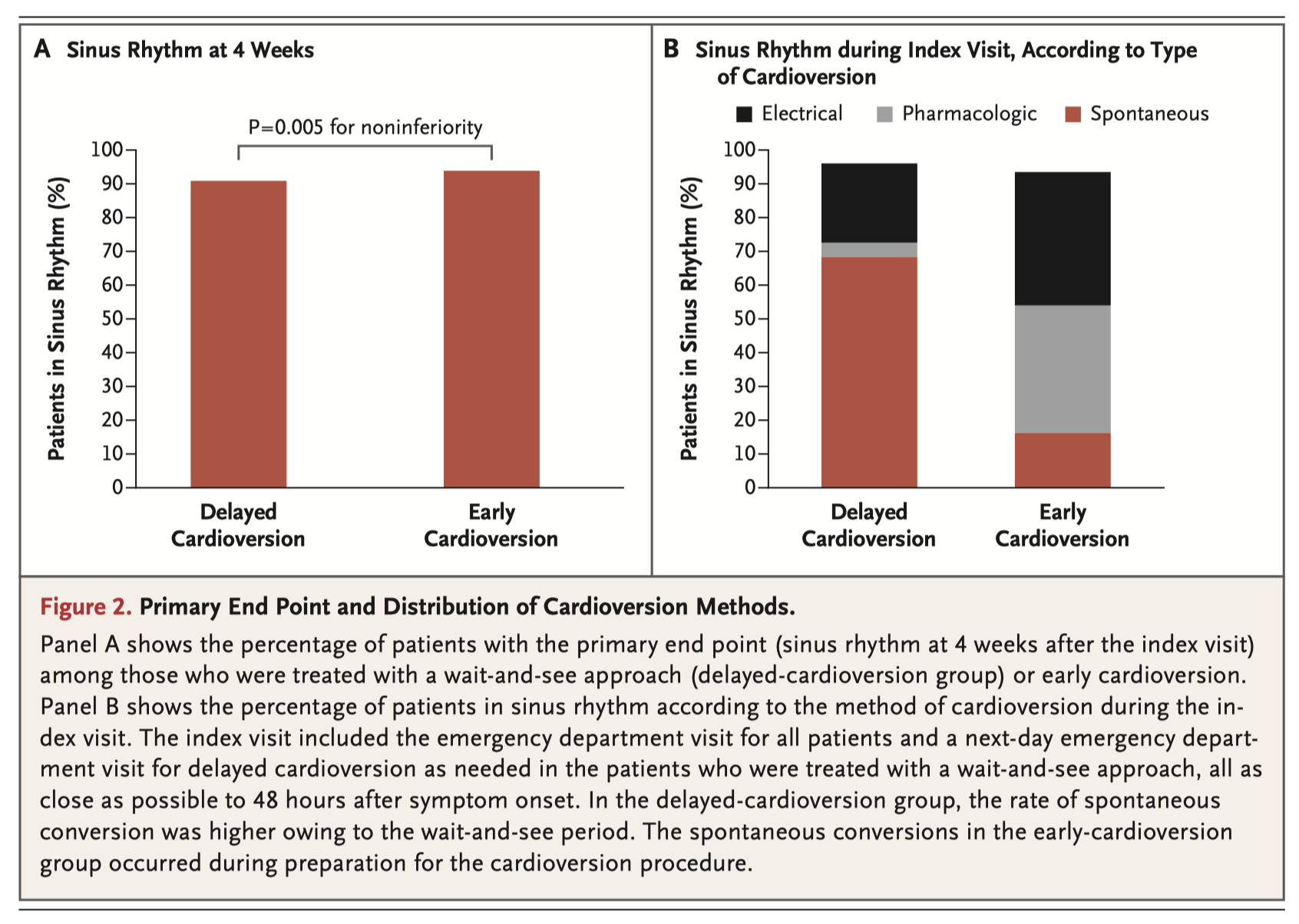
This multicenter non- inferiority trial found no difference in the rate of atrial fibrillation (AF) at four weeks between patients who received early and delayed cardioversion. 437 patients presenting to Emergency with symptomatic, recent onset (<36 hours), and hemodynamically stable AF were randomised to the standard-of-care early group, or delayed group (rate control medication alone, cardioversion if no return to sinus rhythm within 48 hours). The rate of spontaneous reversion of AF was 16% for the early group, and 69% for the delayed group. At four weeks, there was no difference in the rate of sinus rhythm (94% for the early group vs. 91% for the delayed group, P = 0.005 for non-inferiority). Findings are summarized in this Quicktake Video from the journal website.
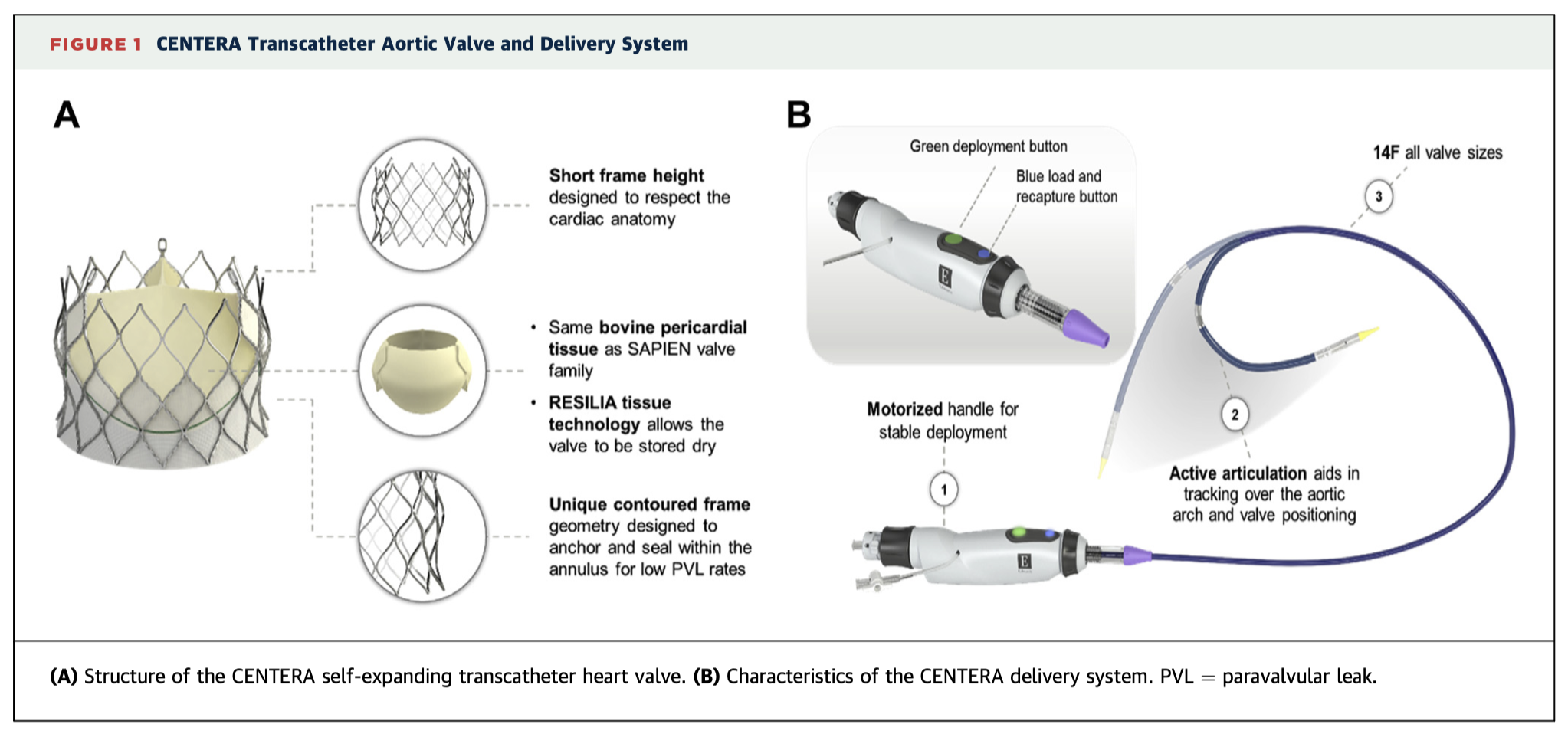
One-year outcomes from 203 patients with severe aortic stenosis who received the CENTERA self-expanding transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) show continued safety and efficacy in a high-risk patient cohort. Echocardiographic outcomes (Central Illustration) were stable, with no incidences of severe or moderate aortic regurgitation. Other outcomes were similar to or better than comparable TAVR devices, with overall incidence of disabling stroke 4.1%, permanent pacemaker implantation 6.5%, cardiac rehospitalisation 6.8%, cardiovascular mortality 4.6%, and overall mortality 9.1%.
Cardiac Surgery
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
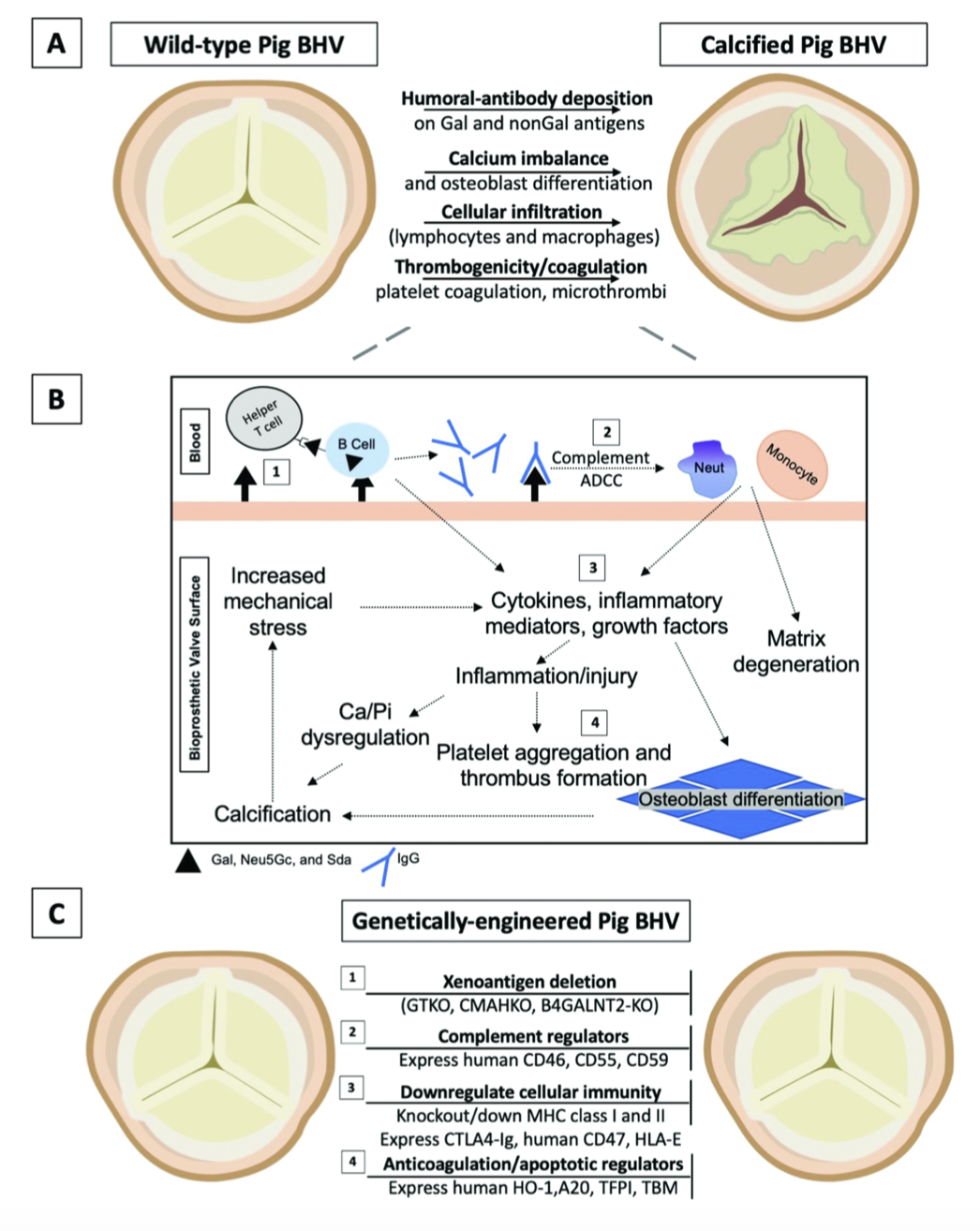
Bioprosthetic heart valves undergo structural degeneration and calcification. Similarities exist in the histopathologic features of explanted bioprosthetic valves and rejected pig tissues and organs after xenotransplantation into nonhuman primates. The current evidence suggests that bioprosthetic valves derived from genetically-modified pigs lacking xenogeneic antigens termed triple-knockout pigs, would function considerably longer than current wild-type (genetically unmodified) porcine valves in human recipients. Preclinical and clinical studies determining the safety and efficacy of triple-knockout porcine bioprosthetic valves will likely establish that they are more resistant to human immune responses and hence less susceptible to structural degeneration.
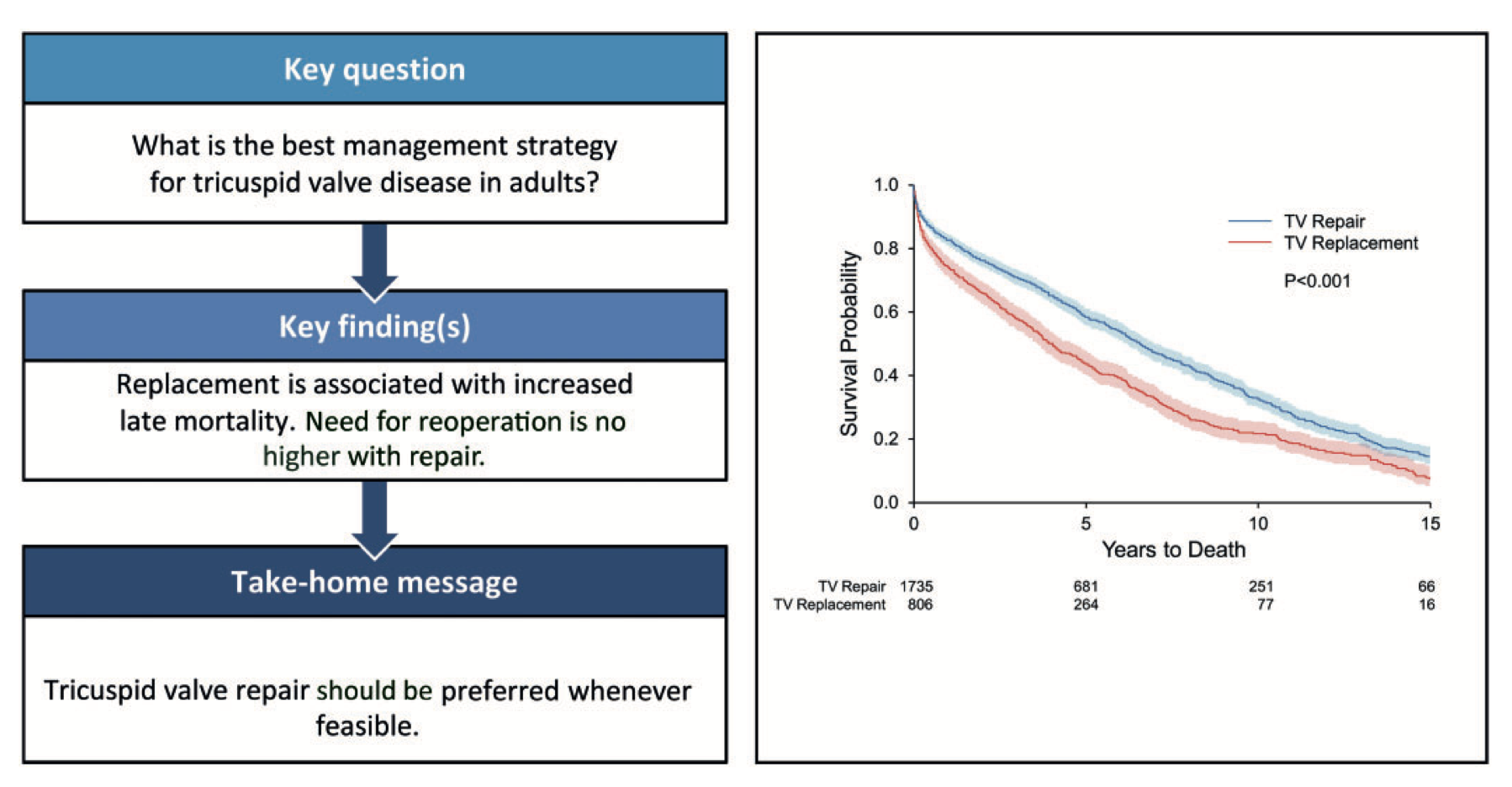
This retrospective analysis studied 2541 patients who underwent first time tricuspid valve (TV) surgery between January 1993 and December 2013, aiming to review the long term outcomes with regard to survival and reoperation. Functional TV regurgitation was present in 54% (n = 1369). A bioprosthesis was used in 84% (n = 680) of replacements, while 54% (n = 934) of TV repairs were ring annuloplasties. Operative mortality was 8% (n = 212). Overall survival was 54%, 29% and 13% at 5, 10 and 15 years, respectively. The authors concluded that TV repair results in better survival compared to replacement in patient with similar comorbidities with no increased risk of requiring reoperation.
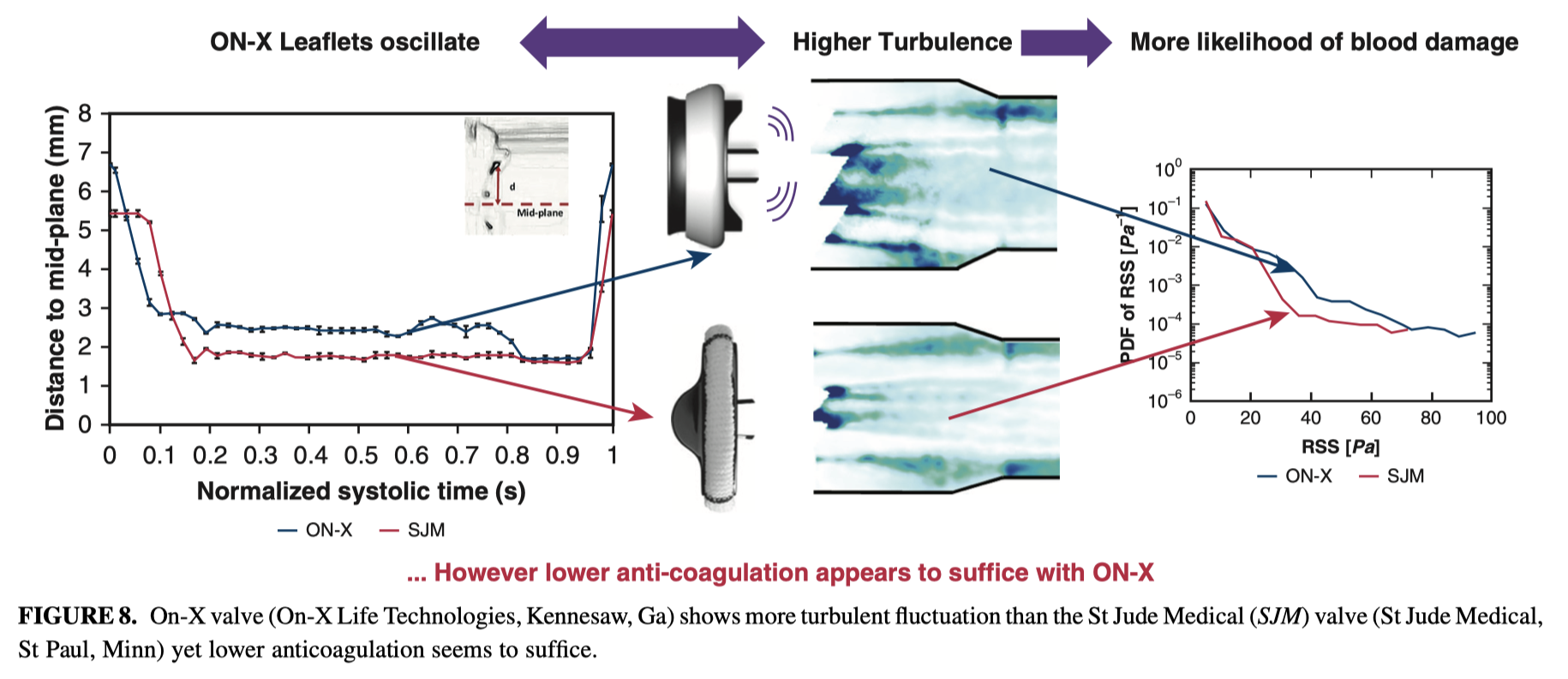
This study aimed to investigate the haemodynamic and turbulence characteristics upon implantation of St Jude Medical (SJM) and On-X bileaflet mechanical valves under pulsatile physiologic conditions. Despite the design differences that characterize On-X mechanical valves and the recent COAPT trial demostrating lower acceptable INR target in the aortic position, the hemodynamic and turbulence parameters were not necessarily improved in comparison with a St Jude Medical valve.
Cardiac Imaging
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
This is an in-depth, pictorial educational review of the anatomy of the interatrial septum and the atrioventricular junction as seen on Cardiac MRI, Cardiac CT, and 2D and 3D echocardiography. Given left-sided catheter based interventions require transeptal puncture, understanding the fine anatomical details of this region is essential for interventional clinicians. Our advances in imaging can now provide additional resolution and perspective, with comparison made to anatomic specimens.
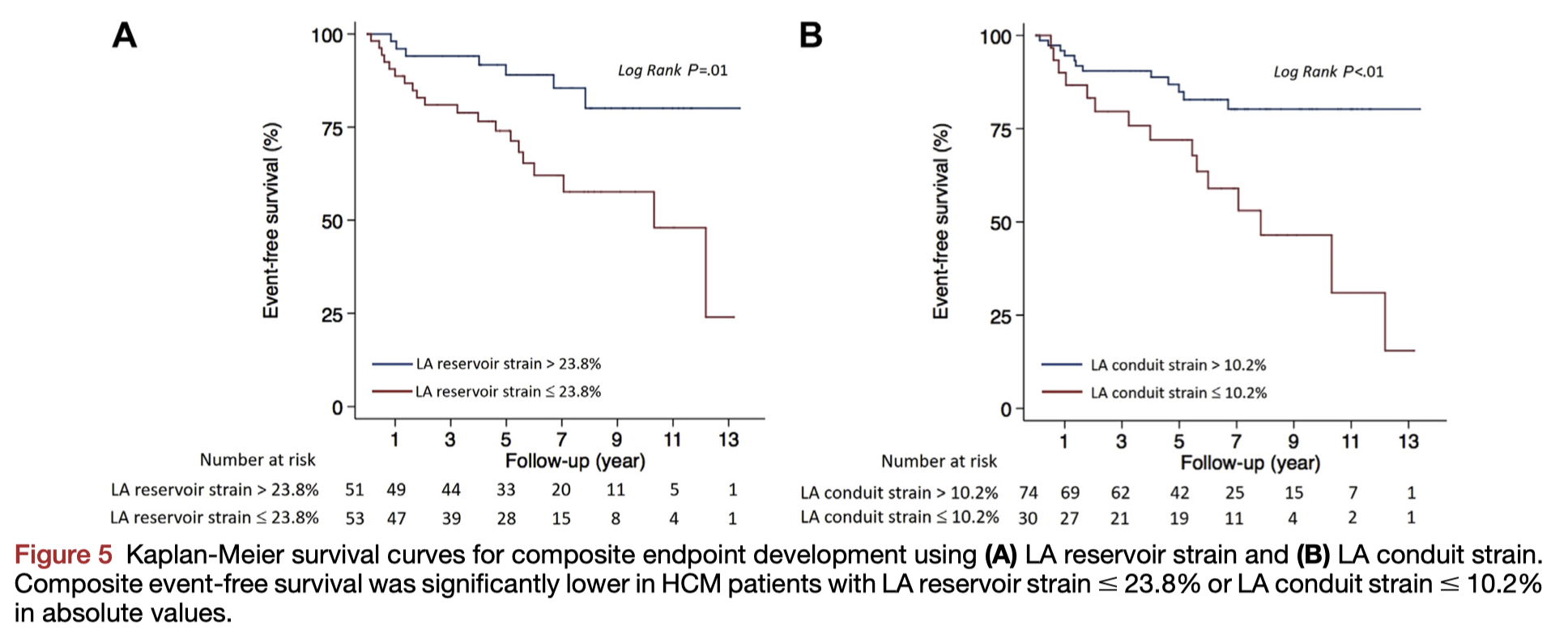
In this retrospective analysis of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), the presence of co-morbid atrial fibrillation (AF, n=45 of 105 total patients) was associated with left atrial (LA) myopathy, indicated by higher volumes, higher strain, and lower LA ejection fraction. These patients were also at higher risk of the composite end point of heart failure, stroke, and death (Figure 5).
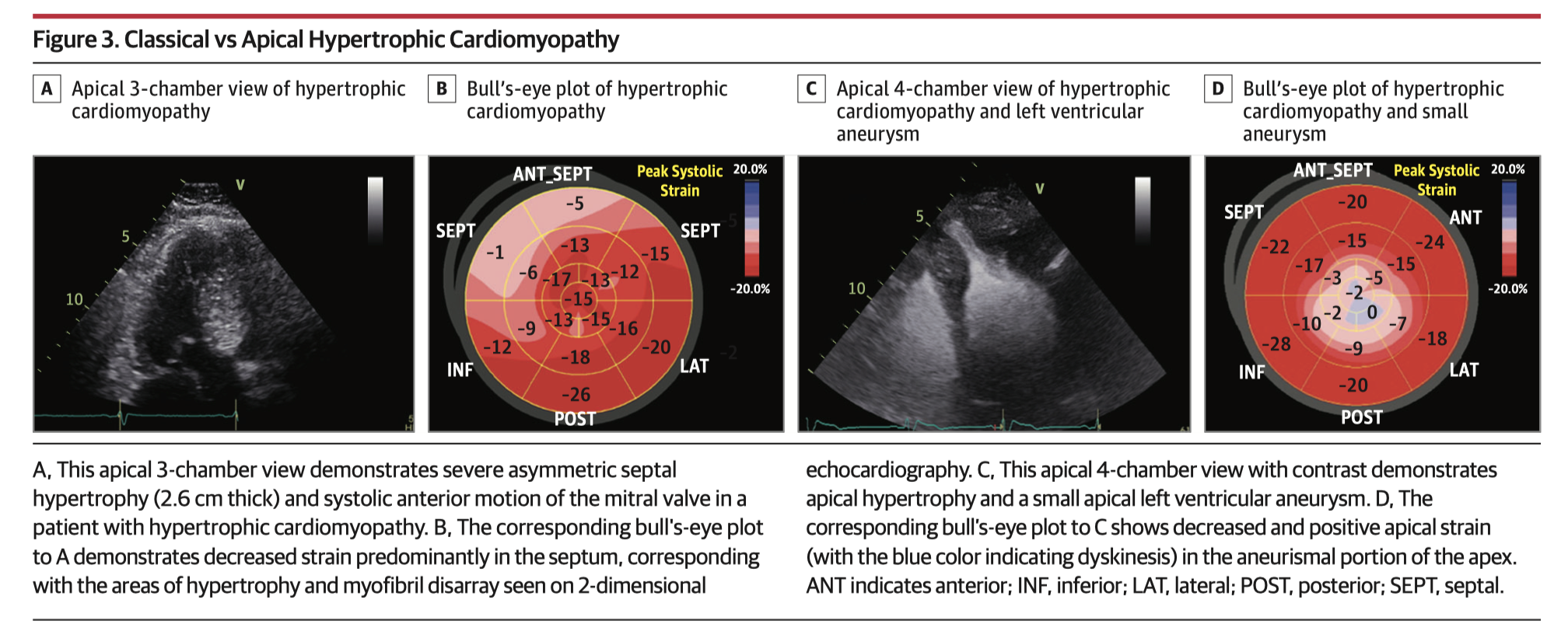
Speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE) analyses myocardial deformation or strain across the cardiac cycle and is used to provide a quantitative measure of myocardial function. This narrative review discusses the characteristic “bull’s eye” patterns of STE in disease states including valvulopathies, cardiomyopathies, and coronary artery disease; and how STE is being used for diagnostic and prognostic evaluation in clinical practice.
Perioperative Medicine
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
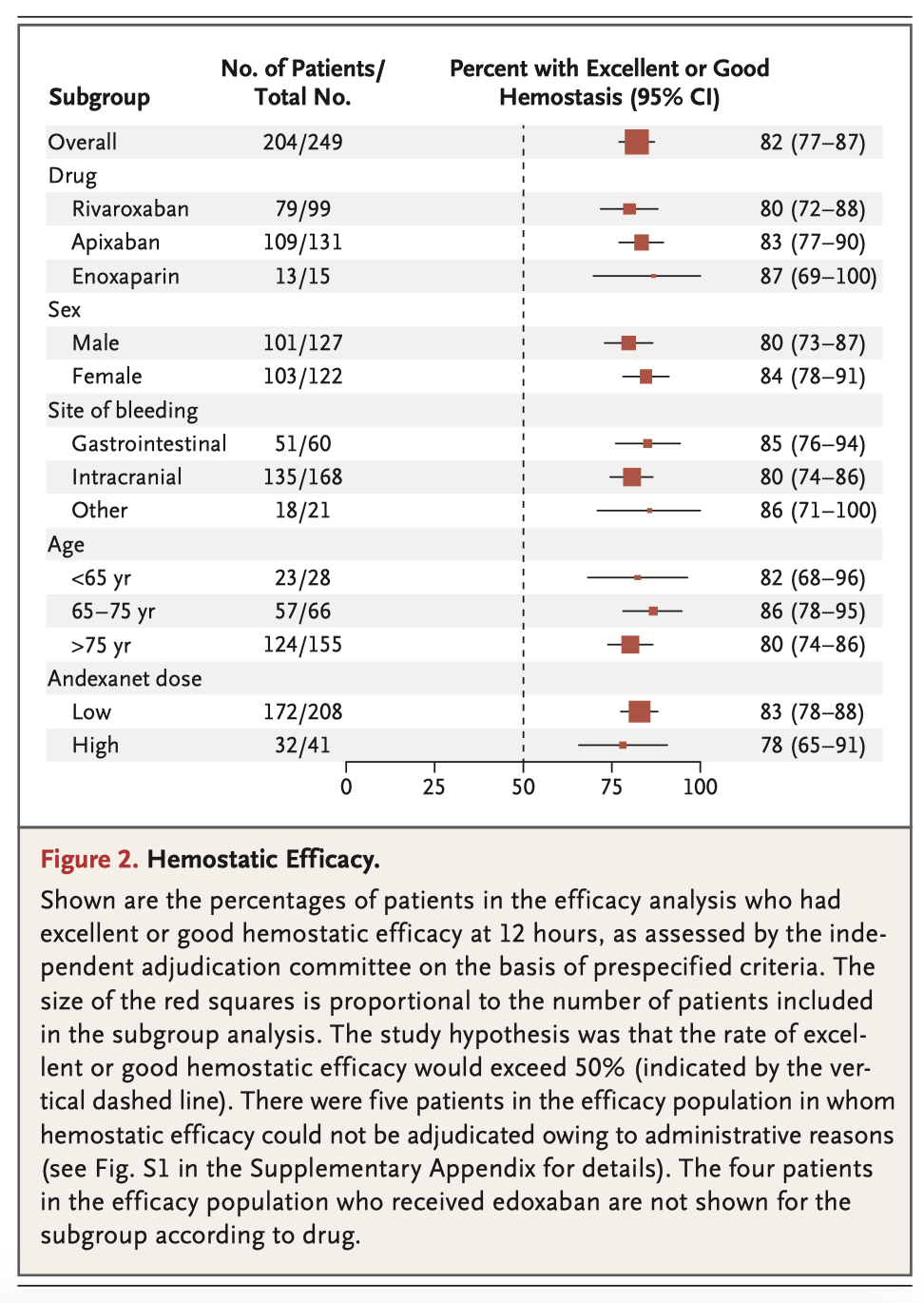
Andexanet alfa is a modified recombinant inactive form of human factor Xa developed for reversal of factor Xa inhibitors. This paper studied 352 patients who had acute major bleeding within 18 hours after administration of a factor Xa inhibitor. Percent change in anti-factor Xa activity and haemostatic efficacy was studied following a bolus dose of andexanet, and a subsequent two hour infusion. In patients with acute major bleeding associated with the use of a factor Xa inhibitor, treatment with andexanet markedly reduced anti-factor Xa activity, and 82% of patients had excellent or good haemostatic efficacy at 12 hours, as dictated by pre-specified criteria.
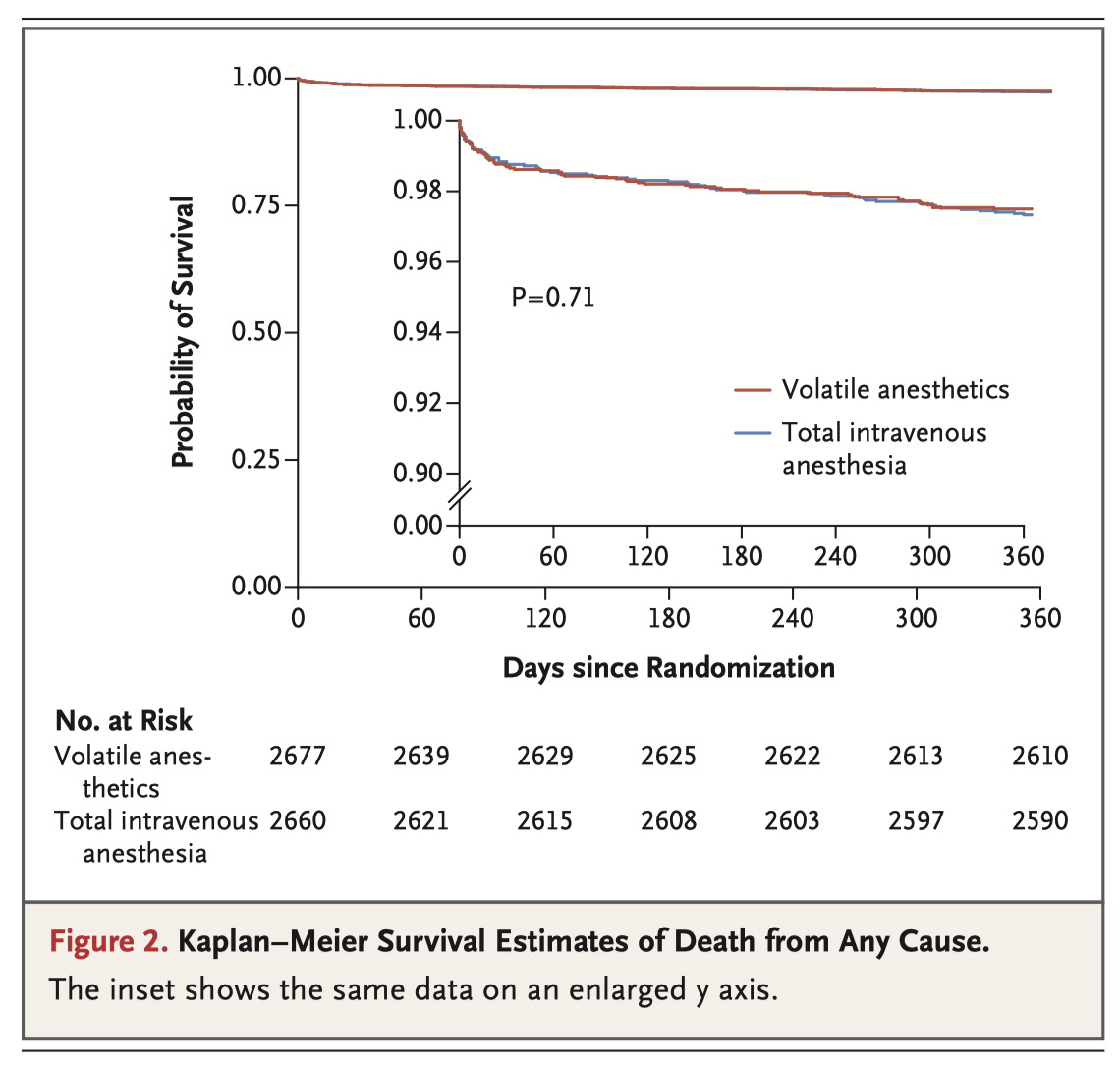
Volatile (inhaled) anesthetic agents have cardioprotective effects, which might improve clinical outcomes in patients undergoing coronary-artery bypass grafting (CABG). In this study, 5400 patients undergoing elective CABG were randomly assigned to receive either a volatile anaesthetic (desflurane, isoflurane, or sevoflurane), or total intravenous anaesthesia. Among patients undergoing elective CABG, anesthesia with a volatile agent did not result in significantly fewer deaths at 1 year than total intravenous anesthesia.
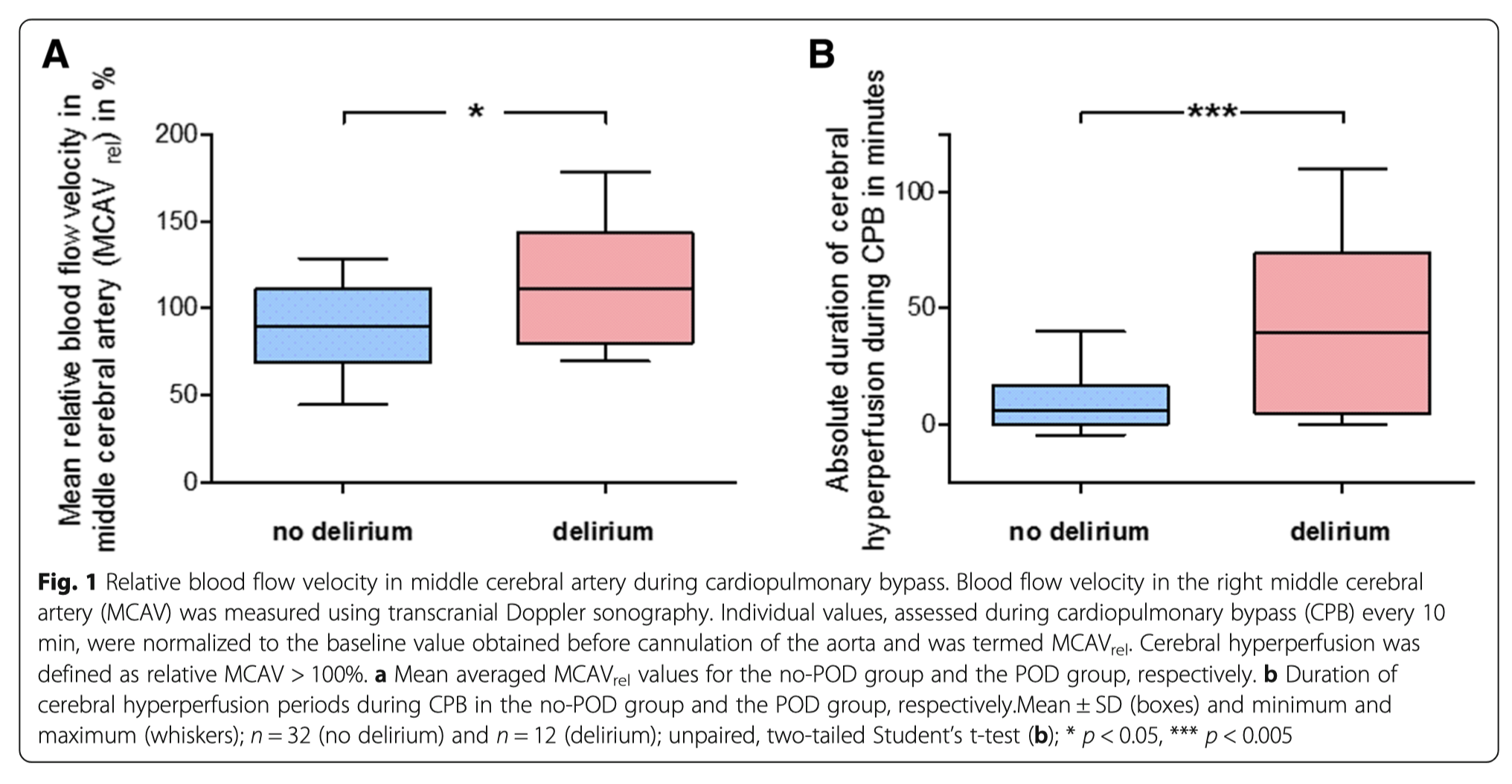
This study of 47 consecutive patients aimed to evaluate if changes in on-pump cerebral blood flow, relative to pre-bypass baseline, were associated with risk for postoperative delirium (POD) following cardiac surgery. Overall prevalence of POD was 27%. In the subgroup without POD, 32% of patients had experienced relative cerebral hyperperfusion during CPB, compared to 67% in the subgroup with POD (p < 0.05). The authors concluded that the results suggest a critical role for cerebral hyperperfusion in the pathogenesis of POD following on-pump open-heart surgery, recommending a more individualized hemodynamic management, especially in the population at risk.