Welcome to the monthly SHDA Research Update. Our specialists have selected 3 seminal papers that have been recently published in each speciality (Cardiology, Cardiac Surgery, Cardiac Imaging, Perioperative Medicine).
Cardiology
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
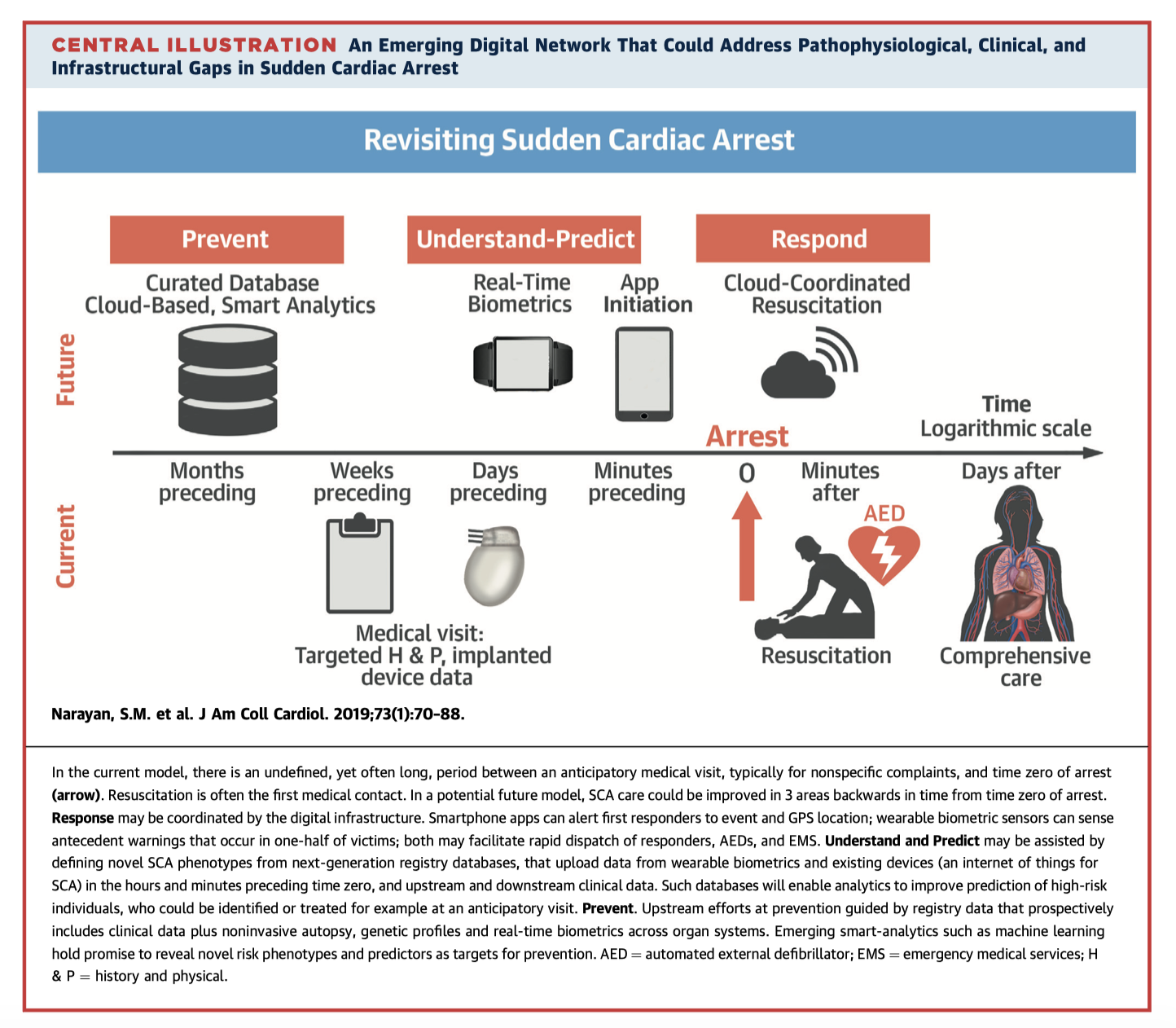
Reducing the mortality of sudden cardiac death (SCD) is difficult given the multiple levels of possible intervention and stakeholders involved. This review summarises these challenges using a framework of (a) prevent, (b) understand and predict, and (c) respond (central illustration). New technologies, such as cloud based big-data for prevention, real-time biometrics to initiate rapid action in the event of arrest, and on-scene apps and assisted resuscitation could have the potential to improve SCD outcomes.
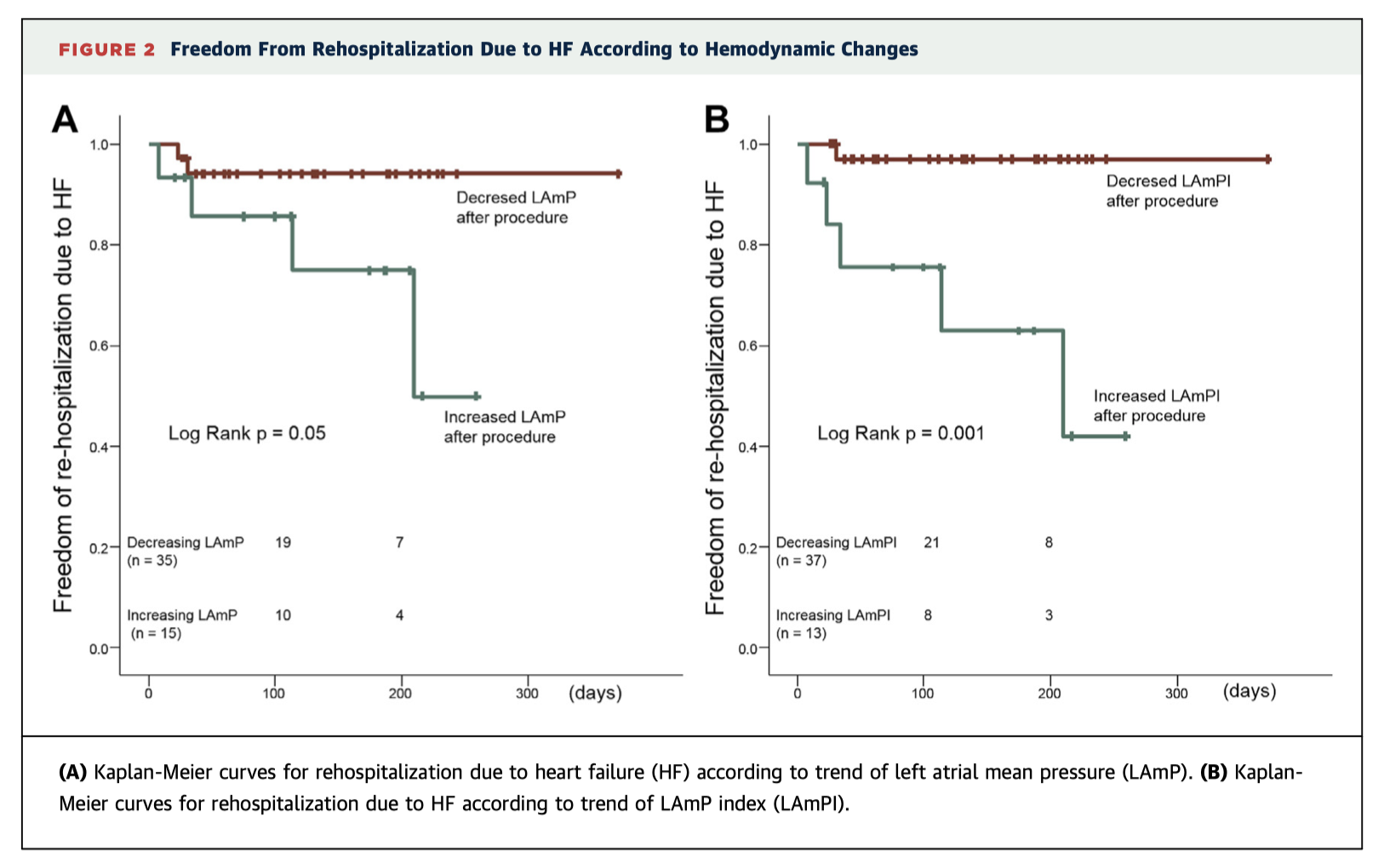
The effectiveness of MitraClip therapy for mitral regurgitation (MR) is traditionally assessed intraoperatively using operator-dependent transoesophageal echocardiography. This prospective trial of 50 patients demonstrates the additional prognostic benefit of real-time monitoring of left atrial pressures to predict clinical outcomes. Higher left atrial mean pressures were significantly associated with rehospitalisation with heart failure (p=0.007) and decreased NYHA functional status (p=0.005) at short term follow-up, independently of echocardiographic findings.
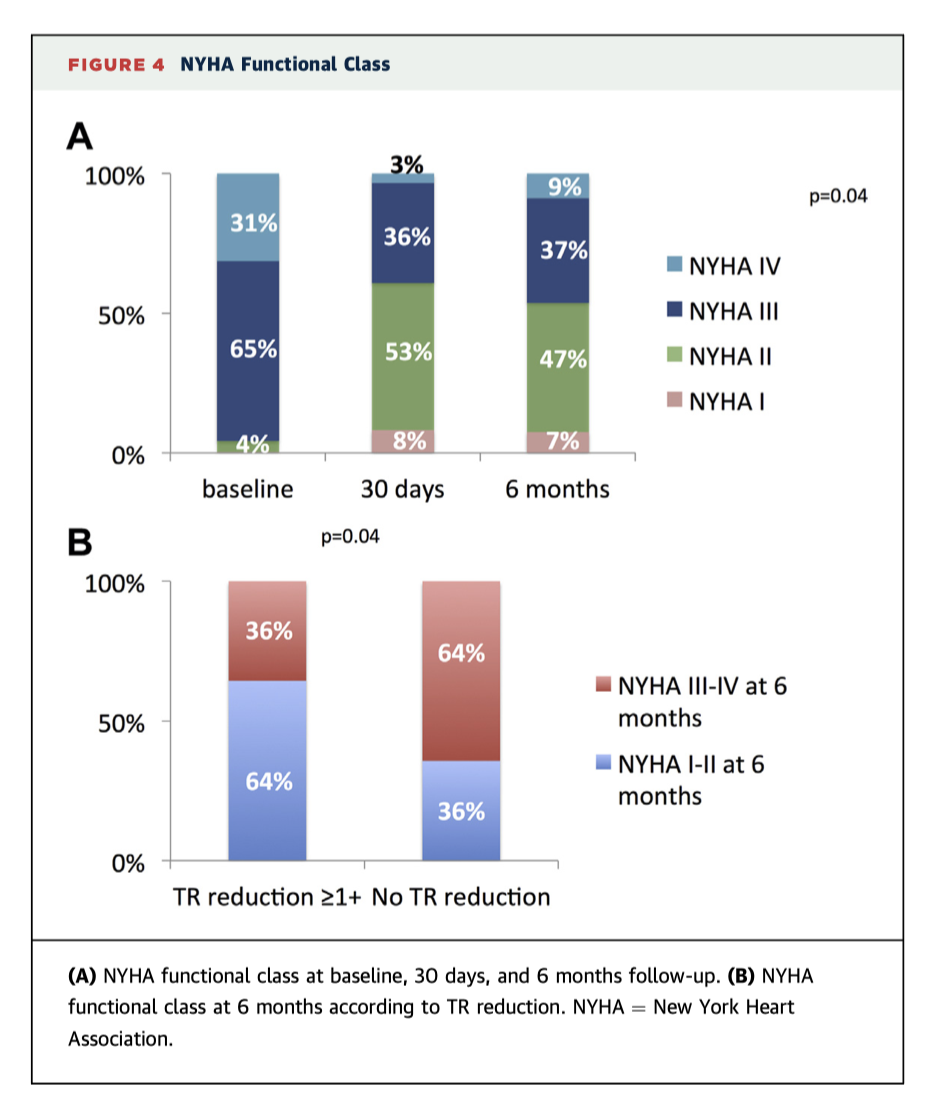
The TriValve Registry is a prospective, multinational initiative following patients with severe tricuspid regurgitation (TR) who have undergone transcatheter tricuspid vale intervention (TTVI) with a range of devices. These midterm outcomes show favourable results overall from 312 patients. Procedural success rate was good (72.8% with no difference between devices, p=0.20), with low 30 day mortality (3.6%), good actuarial survival at 1.5 years (82.8±4%), and significant clinical improvement (Figure 4).
Cardiac Surgery
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
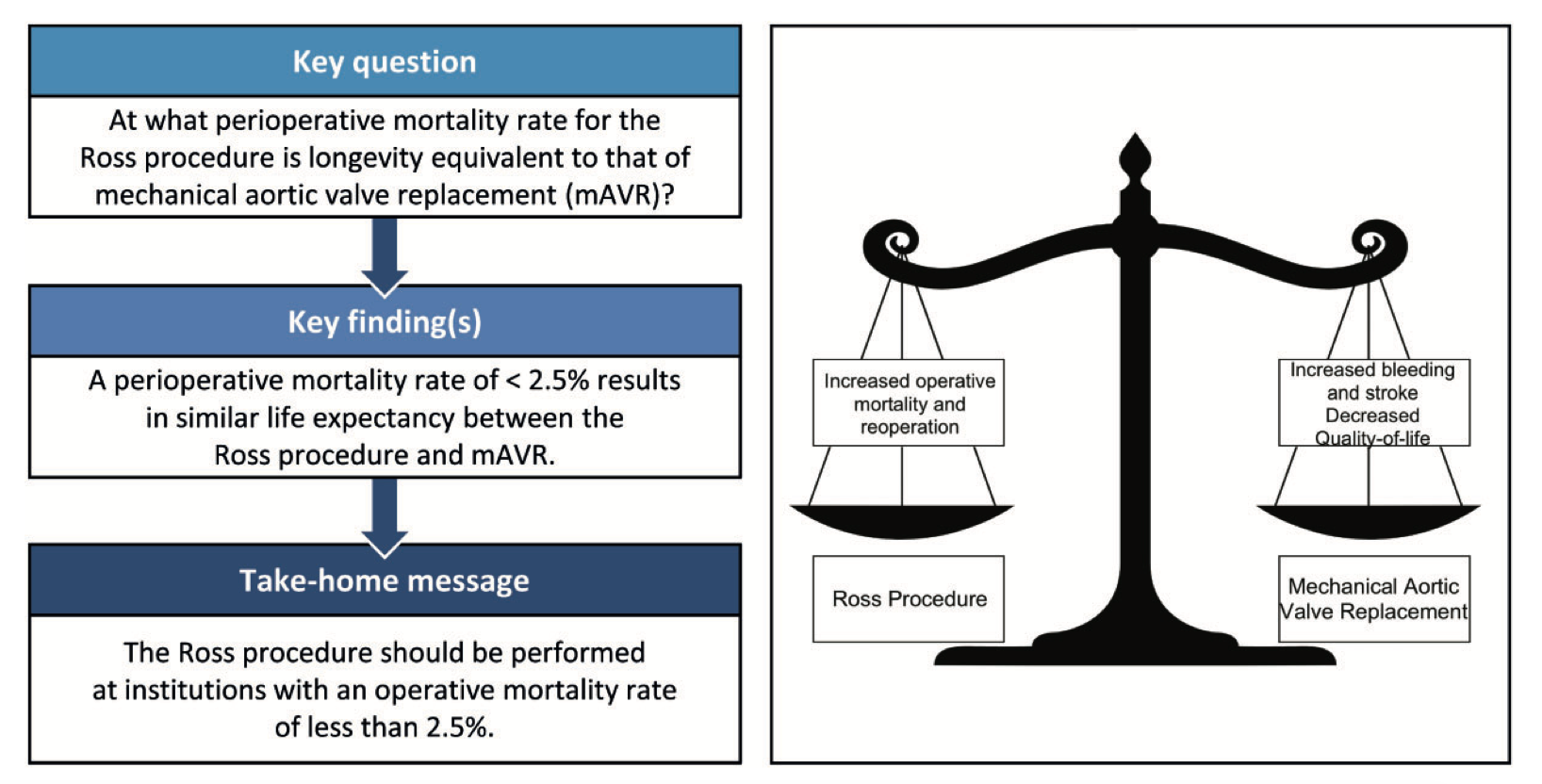
This study aimed to determine the range of perioperative mortality rates associated with the Ross procedure that results in a life expectancy comparable to that seen with mechanical aortic valve replacement (mAVR) in young patients with aortic valve disease. A fully probabilistic Markov microsimulation model was used. The authors concluded that the Ross procedure should be performed at institutions with an operative mortality of less than 2.5%.
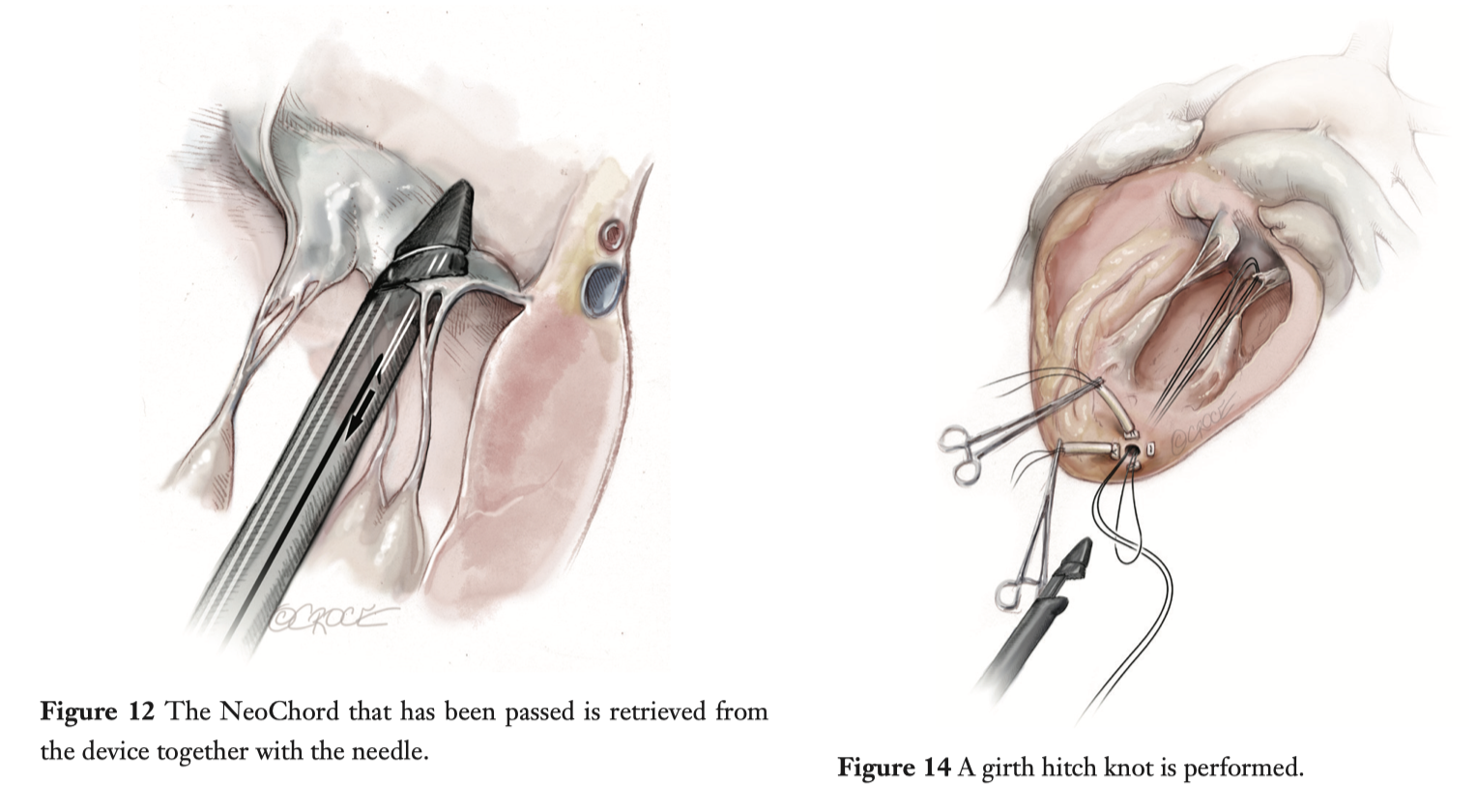
Transapical off-pump mitral valve repair (MVr) with NeoChord implantation has become widely applied in Europe for patients presenting with severe mitral regurgitation due to leaflet prolapse or flail. The procedure is performed under real-time 2D- and 3D-transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) allowing real-time monitoring of haemodynamic recovery. The authors concluded that this procedure has evolved into a reproducibly successful and safe approach.
Cardiac Imaging
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
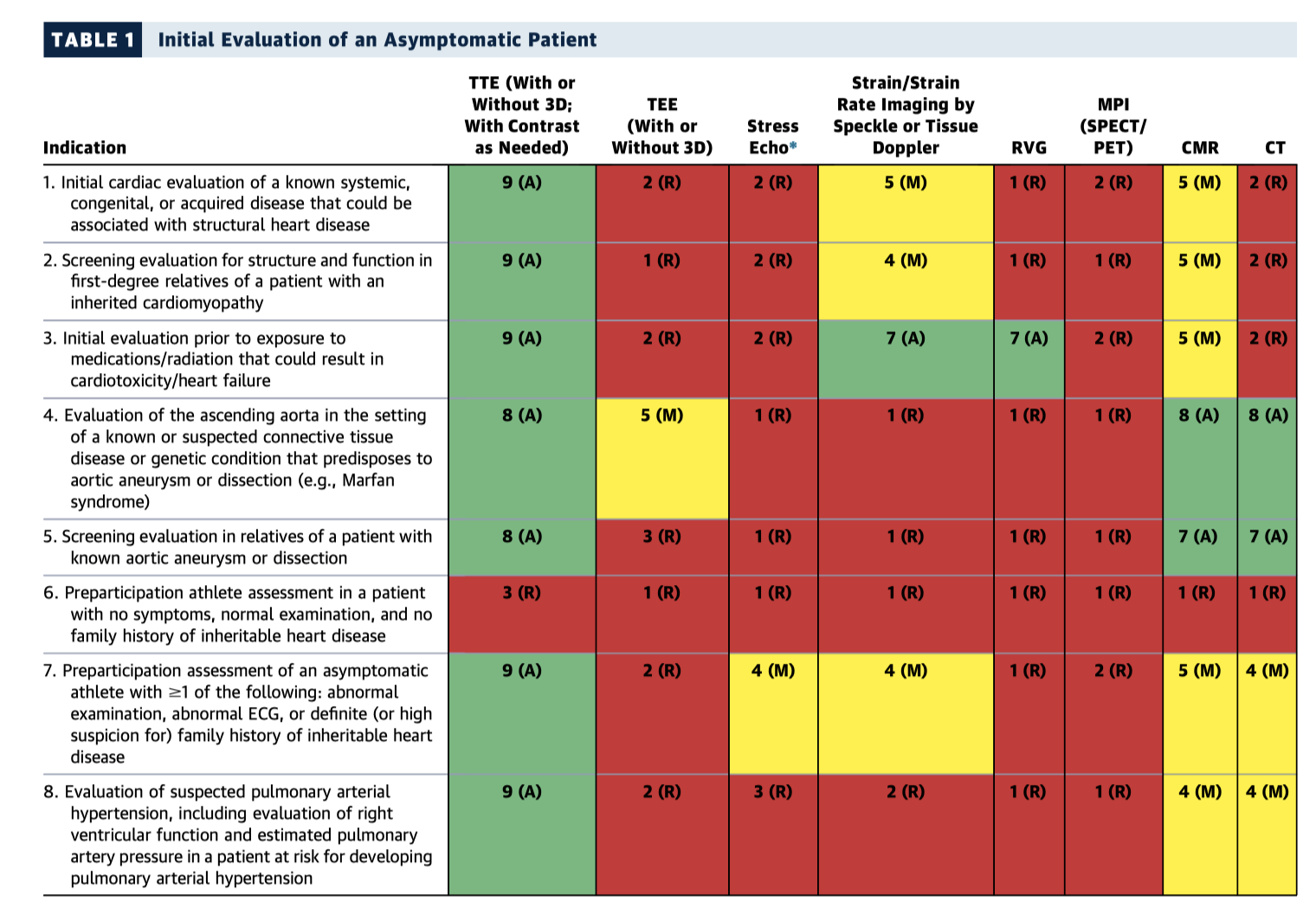
This joint consensus document is organised into 8 tables summarising recommendations for multimodality imaging in the setting of structural (nonvalvular) heart disease. The tables (see Table 1, below, for an example) provide a visually easy to use “traffic light” system according to whether a test is clinically appropriate, as per agreement by the expert panellists. The tables are generally ordered by clinical presentation/situation, including evaluation of new symptoms eg. syncope or dyspnoea, for specific suspected disease entities eg. amyloidosis, and ongoing surveillance and clinical decision making.
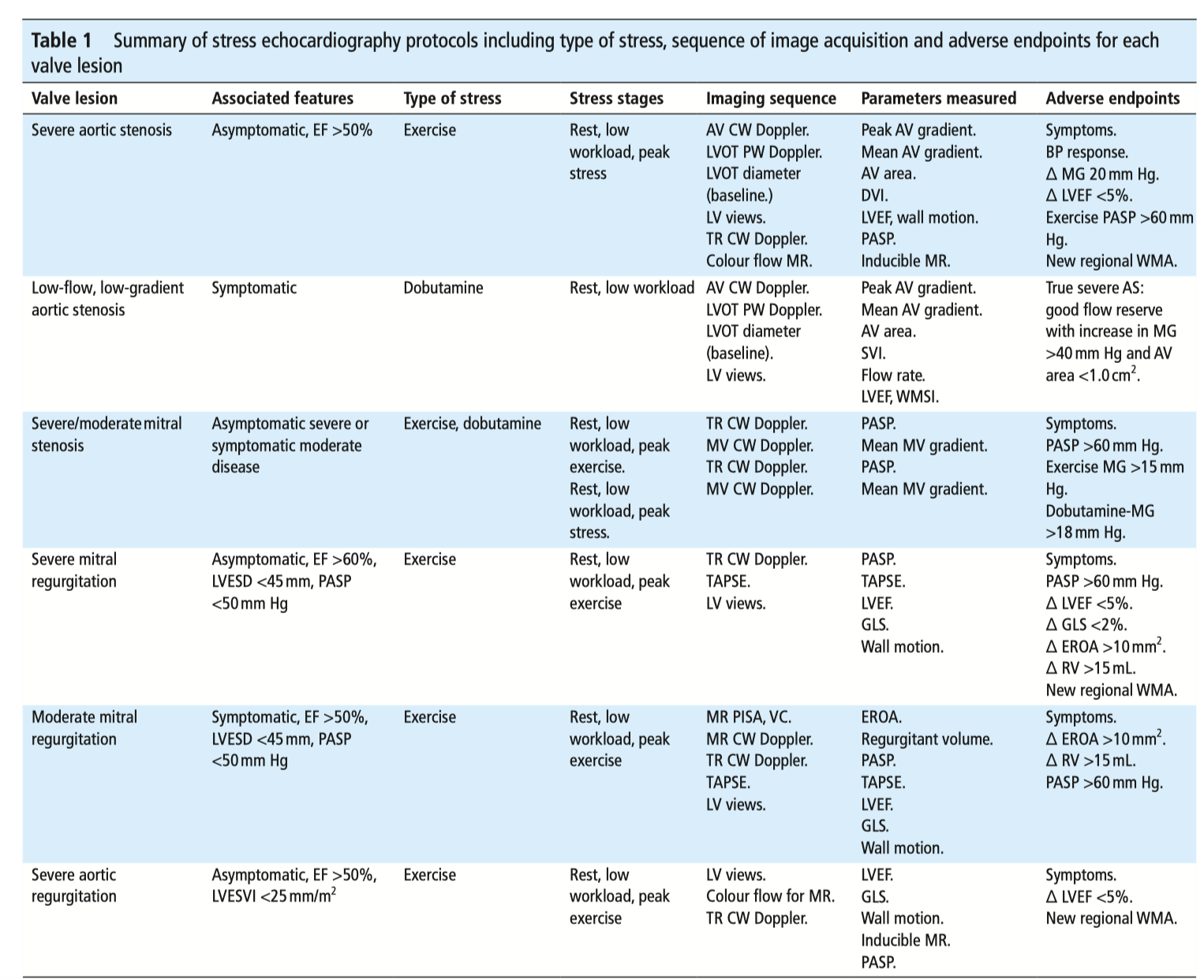
This educational review details the unique role of stress echocardiography is in the evaluation of valvular heart disease. Under exertion, changes in heart rate, loading and compliance influence the haemodynamics across the valve; as such, stress echocardiography is becoming increasingly studied as a modality for functional assessment and to guide optimal timing of procedural intervention. Currently, it has an established role in low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis, and symptomatic moderate MS. While further research is needed, with clinical judgement applied it may provide a useful tool in the assessment of borderline or complex cases.
This well-illustrated expert consensus document provides an overview of aortic valve imaging in the setting of transcatheter aortic valve intervention. The first section details protocols for image acquisition, contrast administration, synchronisation and reconstruction. The majority of the review covers pre- and post-procedural assessment for both native and valve-in-valve implantation techniques, with summary tables highlighting the consensus recommendations for minimum reporting standards.
Perioperative Medicine
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
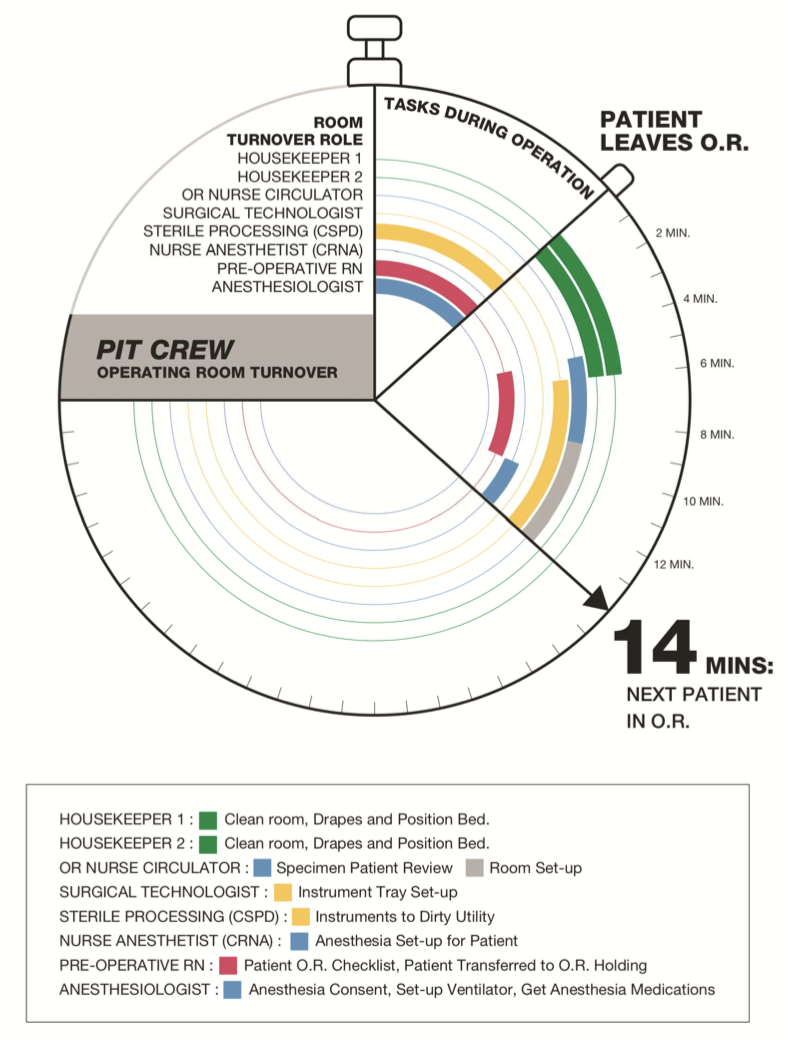
Prolonged operating room turnover time erodes patient and employee satisfaction and value. Lean and value stream mapping was applied to three operating room teams at an academic health centre in New York City and a solution called Performance Improvement Team (PIT Crew) was piloted. The authors concluded that lean and value stream mapping identifies non-valued steps in operating room turnover and affords opportunities for efficiency.
Given their anti-inflammatory properties, corticosteroids have long been administered to cardiac surgery patients in an attempt to mitigate the systemic inflammatory response and potentially improve outcomes. This review provides a succinct review of the latest clinical evidence for prophylactic corticosteroid use in adult and paediatric cardiac surgery. Evidence has shown that little benefit, and potential harm, should question the routine use of steroids in adult populations. Similarly, some evidence in paediatric, and even neonatal populations, suggests prophylactic steroid administration does not improve outcomes and may increase morbidity.
Fluid overload constitutes a major source of morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. This systematic review of 759 patients undergoing cardiac surgery aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tolvaptan in fluid management after cardiac surgery compared with conventional diuretic therapy. The authors concluded that the outcomes of this meta-analysis suggest the promising role of tolvaptan administration in this setting. Future large-scale clinical trials should be conducted to fully elucidate its efficacy and to optimize a clinical protocol.