Welcome to the monthly SHDA Research Update. Our specialists have selected 3 seminal papers that have been recently published in each speciality (cardiology, cardiothoracic surgery, cardiac imaging, perioperative medicine).
Cardiology
Summarised by Sarah Catchpoole
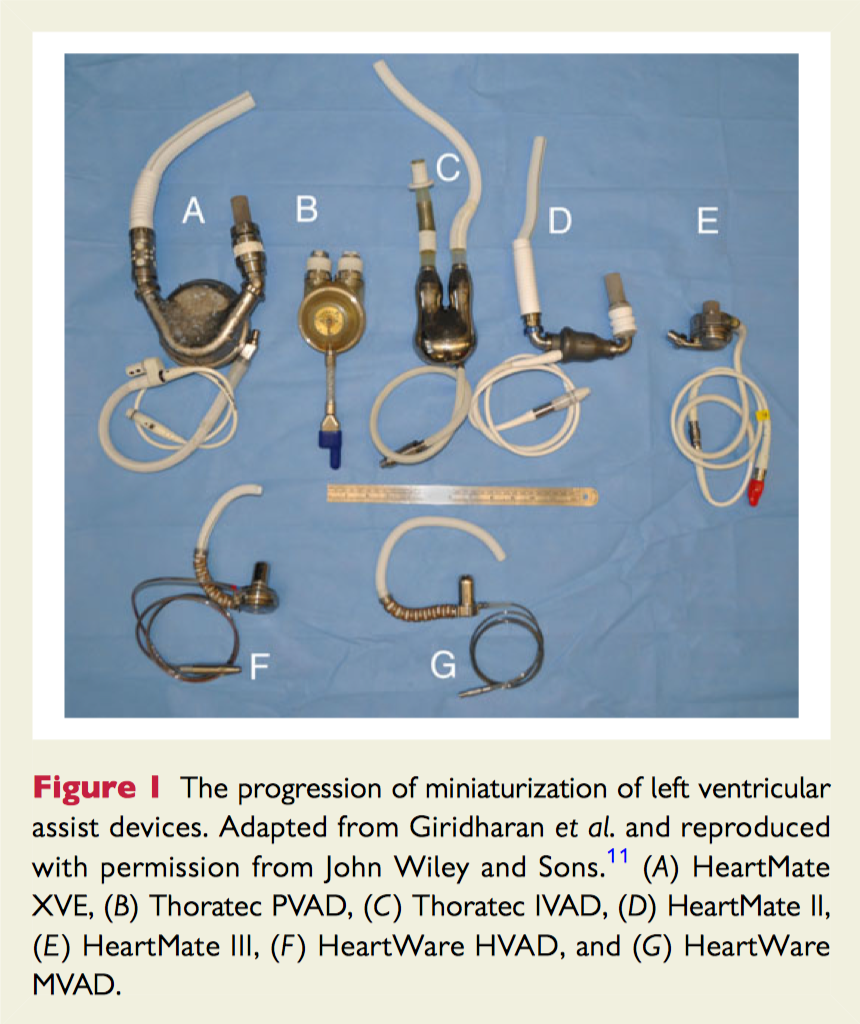
Left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) now have the potential for more widespread application given the considerable technological advances, miniaturisation of devices, improved outcomes, and growing population of patients with advanced heart failure. This review summarises the history and development of LVADs, and reviews current guidelines for implantation. Current controversies are discussed in detail, including evidence for the expansion of indications, continuous vs. pulsatile flow models, quality of life and device complications, and LVADs as therapy for myocardial recovery.
The prognostic value of NT-proBNP in aortic stenosis (AS) is unclear. This prospective cohort study examined 809 patients with both symptomatic and asymptomatic isolated degenerative AS of at least mild severity over 2 years. Determinants of NT-proBNP were found to be multifactorial and complex. It increased with AS severity (p < 0.0001), symptomatic status (p < 0.0001), age (p=0.0008), diastolic function (p < 0.0001), rhythm (p = 0.007) and history of coronary artery disease (p=0.03). However, there was significant overlap between groups and there was no association with AS-related events after adjusting for AS severity (p=0.12). NT-proBNP was measured again at one year for 211 patients; it did not predict event free survival in patients above and below the median (p = 0.86) and univariate analysis revealed changes in levels were not predictive of outcome (p = 0.43). The authors conclude NT-proBNP as a single prognostic factor should be used with caution.
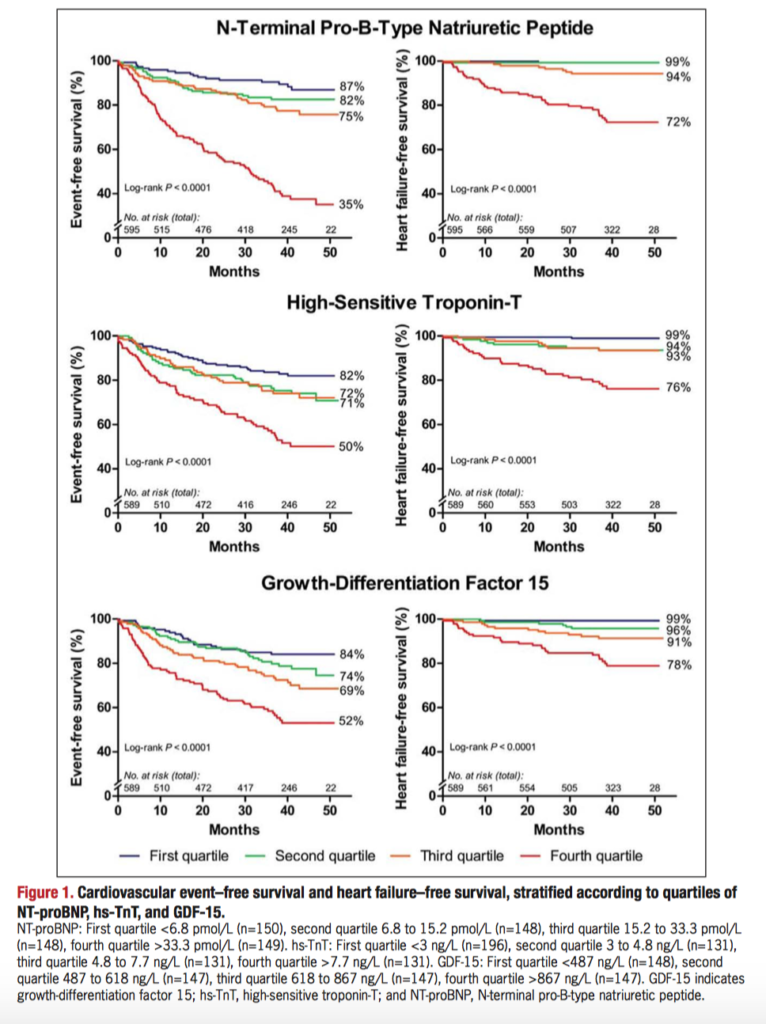
This the first large prospective cohort study to examine the prognostic value of cardiac biomarkers in the growing population of adults with congenital heart disease. 595 clinically stable patients had levels of NT-proBNP, high-sensitive troponin-T, and growth-differentiation factor 15 measured on enrolment and were followed for a median of 42 months. Figure 1, below, shows Kaplan-Meier curves for cardiovascular event–free survival and heart failure–free survival for quartile bands of the three biomarkers. NT-proBNP was the most strongly associated with adverse cardiovascular events, (adjusted hazard ratio, 9.05, P<0.001) and with death or heart failure (adjusted hazard ratio, 16.0, P<0.001). NT-proBNP was also strongly negatively predictive; in patients with low NT-proBNP (<15.2 pmol/L), the cumulative proportion of death and heart failure was 1%. Elevation of all three biomarkers predicted patients at the highest risk. The authors suggest NT-proBNP can be used a screening tool for risk stratification, with low values reassuring and potentially requiring less frequent monitoring. High-risk patients can be further differentiated by the addition of high-sensitive troponin-T, and growth-differentiation factor 15.
Cardiothoracic Surgery
Summarised by Andrew Haymet
The 2 year follow-up results of the Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network (CTSN) severe and moderate ischaemic mitral regurgitation trials demonstrated that nearly half of alive mitral repair patients developed recurrent MR, with a low proportion developing severe MR. Accordingly, the American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) 2015 Guidelines have been updated. In patients with severe MR with a basal aneurysm/dyskinesis, significant leaflet tethering, or severe LV dilatation and being symptomatic despite optimal medical and device therapy, MV replacement is reasonable. MV repair with an undersized annuloplasty ring is otherwise advised in the absence of tethering, akinesis or LV dilatation. For patients with moderate IMR undergoing CABG, MV repair with an undersized complete annuloplasty ring may be considered, rather than being mandatory as per previous Guidelines.
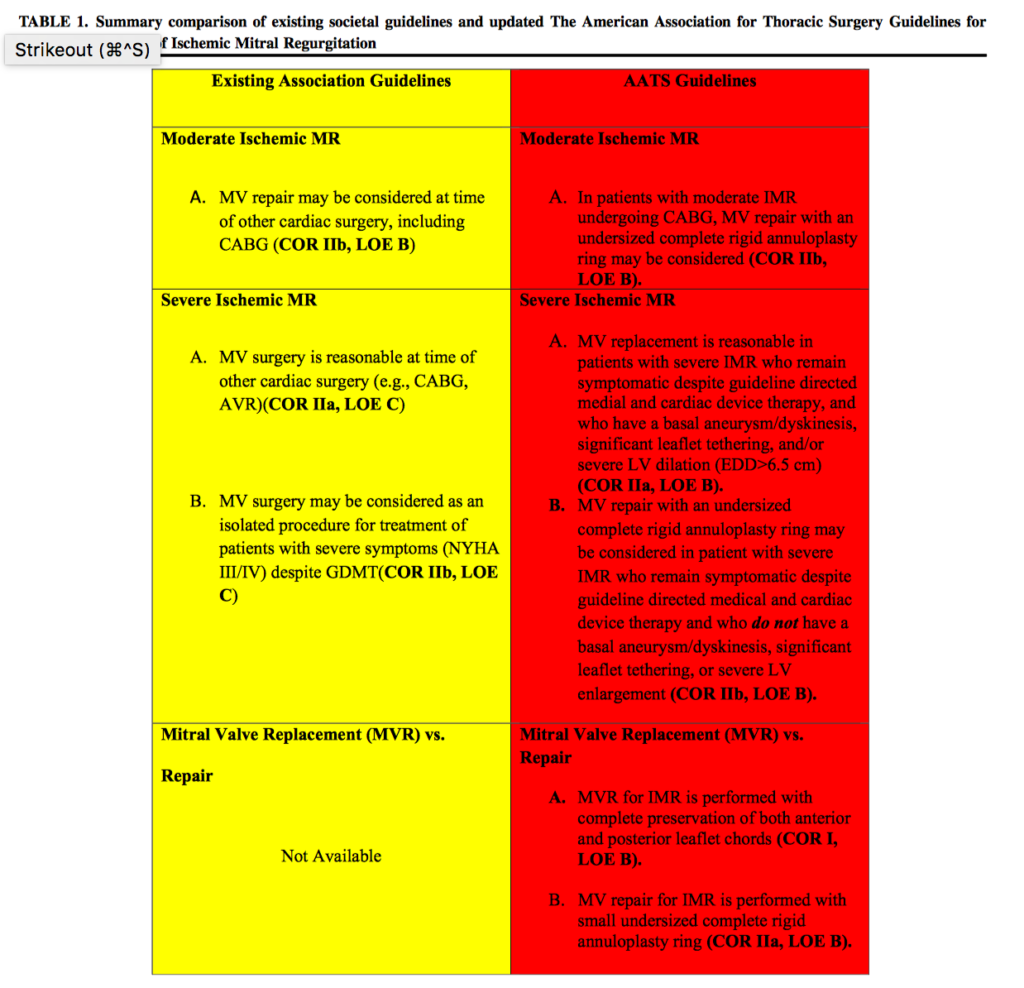
Whilst the isolated tricuspid valve (TV) operation is relatively technically uncomplicated, it is not without operative risk, particularly in those patients receiving a redo median sternotomy. There are inherent risks associated with exposing the caval veins during a TV operation because of their associated dense adhesions. Eight patients who underwent isolated TV operations by minimally invasive thoracotomy between August 2015 to January 2016 were studied. Single femoral cannulation with vacuum-assist was used with acceptable clinical effect, obviating the need for the vena cavae to be snared with the heart beating. Adequate venous drainage was achieved (3.48+/- 0.44L/min) with complete arterial perfusion. Average time of cardiopulmonary bypass was 68.25+/-13.84min. Mean hospital and ICU stays were 4.13+/- 3.52 days and 8.14+/- 4.98. No early in-hospital deaths were recorded. Most vitally, a bloodless and safe surgical field was effectively and reliably created in a significantly simplified procedure.
Transapical approach (TA) is an accepted alternative means of delivering transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) to the conventional transfemoral (TF) technique for symptomatic aortic stenosis. Whilst redo cardiac surgery is associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality compared to the index procedure, the impact of prior CABG on clinical outcome after TA-TAVR remains unclear. In a single centre retrospective cohort analysis, 126 high-risk patients underwent TA-TAVR between October 2010 and December 2014. All cause mortality at 6-months was similar in both groups (11.4 vs 17.3%, p=0.44) and one-year survival was 81.8 and 77.8% respectively. The only multivariate predictor associated with one year mortality was prior stroke (HR 2.76, CI 1.06-7.17, p=0.037). Despite greater baseline risk, patient with prior CABG undergoing TA-TAVR had comparable clinical results in-hospital, at 6 months and at one year compared to those without prior CABG.
Cardiac Imaging
Summarised by Sarah Catchpoole
This brief report demonstrates successful use of the EchoNavigator®-system (Philips Healthcare), in 3 patients with functional tricuspid regurgitation who underwent of transfemoral tricuspid valve clipping. Because the EchoNavigator®-system is able to merge echocardiographic and fluoroscopic images in real time, targets identified on echocardiography can be displayed over fluoroscopic images intraprocedurally, guiding clip placement. The authors suggest this system could increase the chance of procedural success, especially for the less experienced.
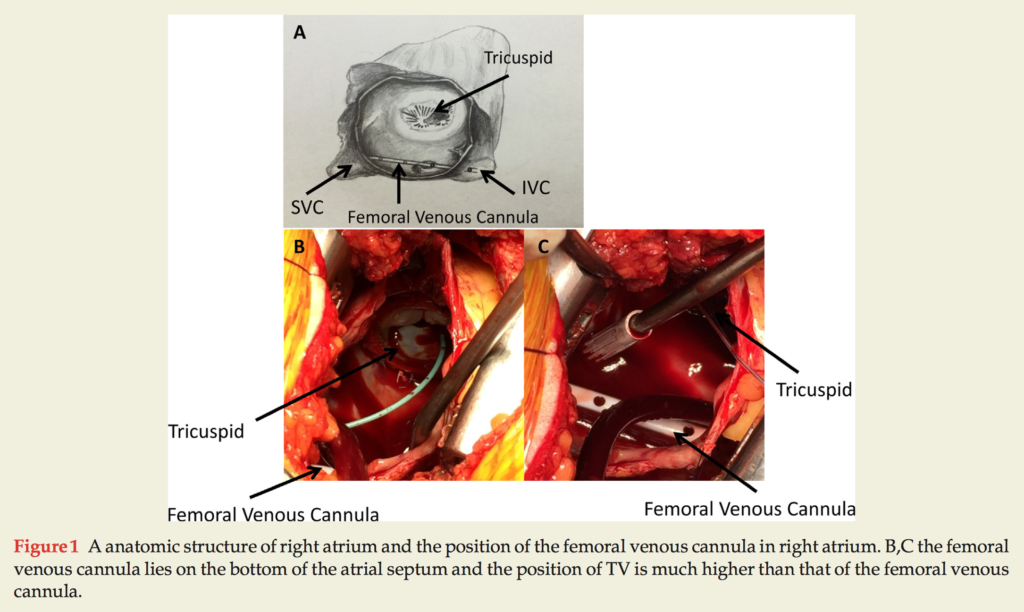
Percutaneous mitral valve (MV) repair can be considered where a patient is deemed to be at high surgical risk. While use of two MitraClips is common, fewer than 5% of cases require three, and there is no record in MitraClip Asia-Pacific Registry of a case using four or more clips. This case report demonstrates the first Australian case to require four MitraClips to successfully treat severe mitral regurgitation (MR) in a 68 year old man with NYHA class III symptoms despite medical therapy. At 2 month follow up, the patient reported improved exercise tolerance and had only mild MR demonstrable on echocardiogram.
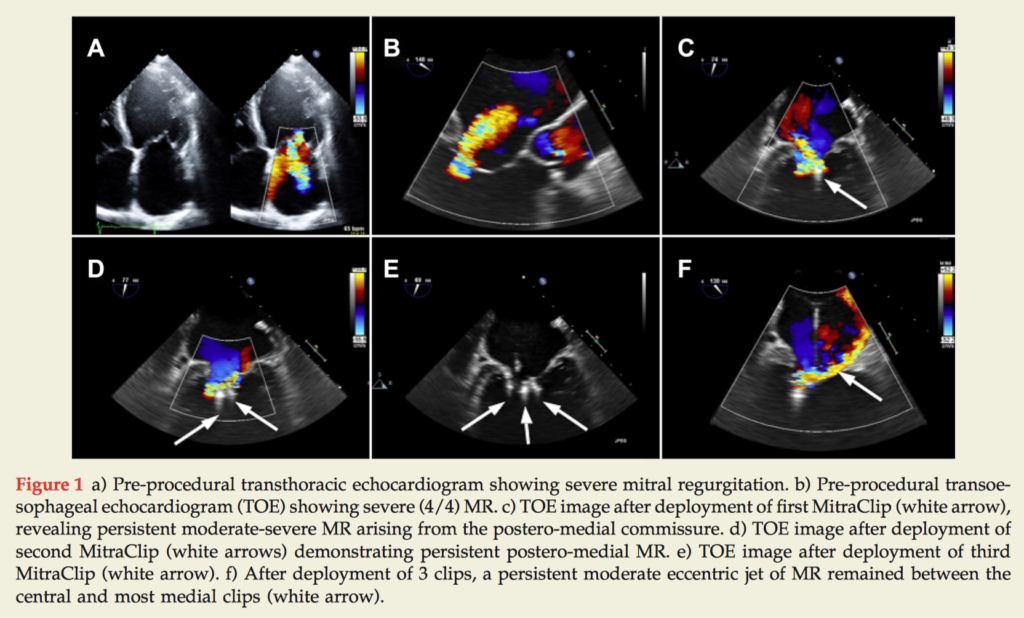
Optimal measurement of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) is an area of controversy, especially as it contributes to grading of measurement of aortic valve area (AVA) in aortic stenosis (AS). In this retrospective study, 58 patients with AS underwent 2D and 3D transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE), taking 3 measurements in the 8 mm proximal to the aortic valve. 3D TTE revealed a funnel-shaped morphology in >80% of patients, becoming more pronounced further from the annular plane. The best agreement between 2D and 3D imaging was at the hinge point of the aortic valve. Because the continuity equation for measurement of aortic valve area (AVA) assumes a circular rather than an elliptical LVOT, the authors suggest 2D measurement at the hinge point is best for reducing measurement error.
Perioperative Medicine
Summarised by Andrew Haymet
The use of left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) has gained significant traction in the treatment of end stage heart failure. Whilst fast-track procedures for other types of cardiac surgery are commonplace, their effects post LVAD implantation remain unclear. This propensity matched study of 53 patients undergoing LVAD implantation between March 2010 and March 2012 sought to test the hypothesis that in-theatre or up to 4 hours postoperative extubation was feasible in INTERMACS level 3 and 4 patients. Patients in the fast track group had significantly lower incidences of pneumonia (p=0.031) and right ventricular failure (RVF, p=0.031). In this group, cardiac index was also significantly higher in the first 12 hours (p=0.017), with a significantly lower central venous pressure postoperatively (p=0.005) and a significantly ICU stay (p=0.016). Four year Kaplan-Meier analysis showed no significant difference in survival. Further prospective randomized studies should investigate preservation of RV function in greater numbers, and further refine selection criteria.
Milrinone is a bipyridine methyl carbonitryl phosphodiesterase-III inhibitor which downregulates the degradation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), increases intracellular cAMP and then increases activation of protein kinase A. Its cardiac effects include positive inotropy and improved diastolic relaxation. In this systematic review and meta analysis of 537 patients from 12 randomized controlled trials assessed the effect of milrinone on short term mortality in adult cardiac surgery patients. The primary outcome was any short term mortality. No difference in mortality rates in patients who received milrinone versus patients who received a comparator was observed (OR=1.25, 95% CI 0.45-3.51, p= 0.67). The wide variations in odds ratios suggest that a simple pooled meta analysis was insufficient to establish the risk and benefit of milrinone administration in this cohort.
This single institution, prospective cohort study aimed to investigate the prevalence and impact of abnormal respiratory patterns in 454 patients undergoing elective coronary artery bypass grafting. Preoperative pulmonary function tests were performed and abnormal respiratory patterns were defined as obstructive (forced expiratory volume in 1 s [FEV1]/forced vital capacity [FVC]<0.70), restrictive (FEV1/FVC≥0.70 and FVC<80% of predicted), and mixed (FEV1/FVC<0.70 and both FEV1 and FVC<80% of predicted). Of the 423 patients, 57 obstructive, 46 restrictive and 4 mixed patterns were newly classified, or 24.6% of cases. Obstructive lung disease was associated with prolonged ventilation time (16 hours or longer), and a reduced FEV1 was associated with an increased likelihood of atrial fibrillation (1-L decrement, odds ratio: 1.38, 95% confidence interval: 1.01 to -1.90,p=0.04) and hospitalization time (regression coefficient: 1.23, 95% confidence interval: 0.54-to-1.91, po0.001). Underdiagnosis of abnormal respiratory patterns is common in cardiac surgery, and preoperative pulmonary function testing may help mitigate risk of complications.