Welcome to the monthly SHDA Research Update. Our specialists have selected 3 seminal papers that have been recently published in each speciality (Cardiology, Cardiac Surgery, Cardiac Imaging, Perioperative Medicine).
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
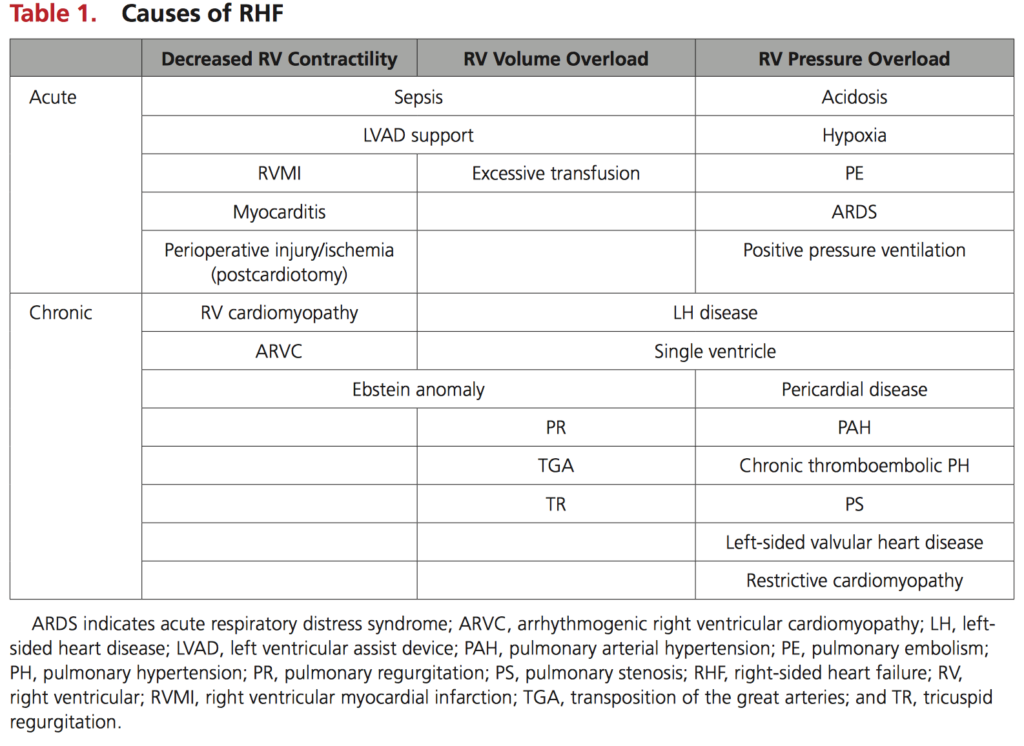
Right heart failure (RHF) is a complex clinical entity with diverse causes (Table 1), and commonly misunderstood. This new scientific statement provides a comprehensive guide to the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, management and clinical challenges of RHF. Subsections of note include pulmonary arterial hypertension, cardiorenal and cardiohepatic syndrome, and an extensive section on medical therapies in acute and chronic RHF. The authors hope to improve clinician’s understanding and therefore management of conditions causing, and caused by RHF.
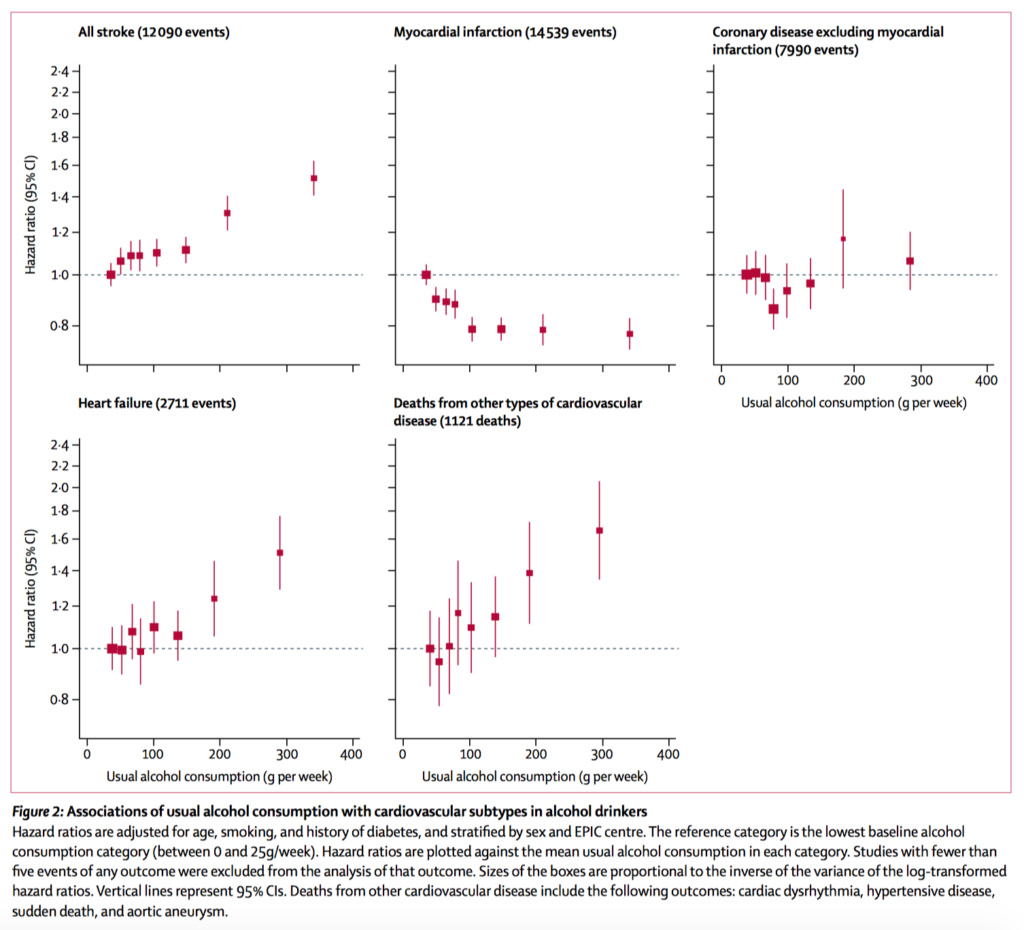
This large analysis of individual participant data from three registries suggest many current national alcohol consumption guidelines should be revised in light of the overall and cardiovascular risks. Examining data from 599 912 current drinkers from high-income countries over 5.4 million person-years of follow-up, the lowest mortality risk was for those consuming below 100g of alcohol per week (10 Australian standard drinks). While alcohol was protective for myocardial infarction, it was linearly associated with increased risk of other coronary disease, heart failure, fatal aortic aneurysm, fatal hypertensive disease, and all stroke (Figure 2), suggesting no safe consumption threshold.
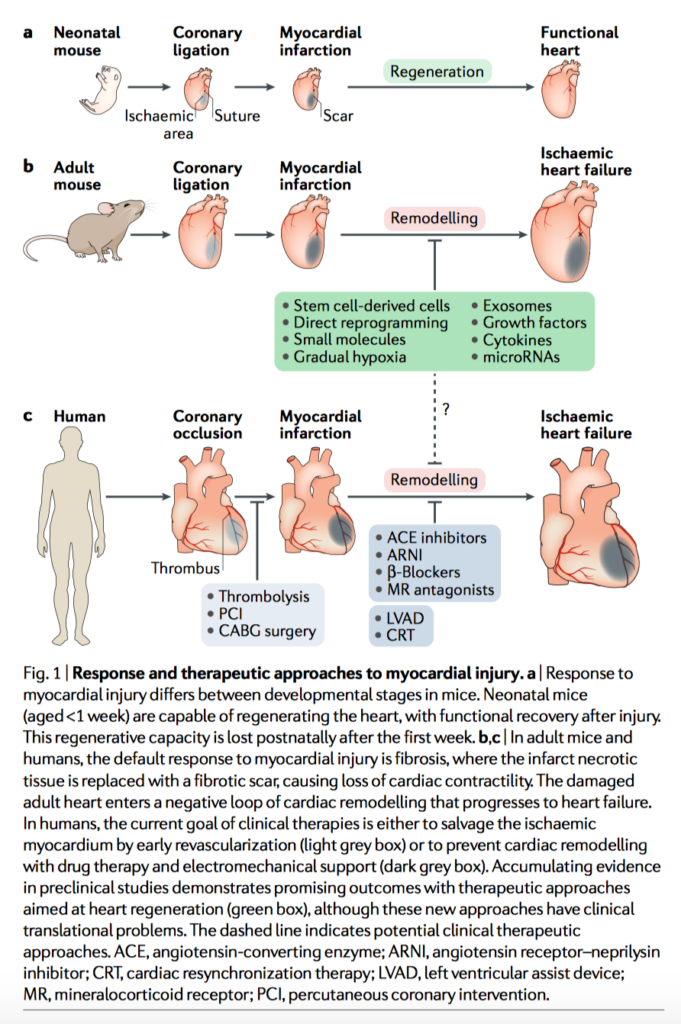
Human cardiac myocytes have minimal ability to regenerate and therefore therapies for ischaemic heart disease are typically limited to (a) limitation of tissue infarction/loss in the acute setting and (b) protection of the heart in the progression to fibrosis, dysfunction, dilation and cardiac failure. This review examines the status and promise of the emerging therapies in cardiac myocyte regeneration. Findings of pre-clinical trials are summarised in table format, before detailed review of the physiology of potential regenerative mechanisms and stem cell therapies studied to date. However, while significant progress has been made in the laboratory and towards understanding on the cellular and molecular level, much further work is needed before clinical adoption.
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
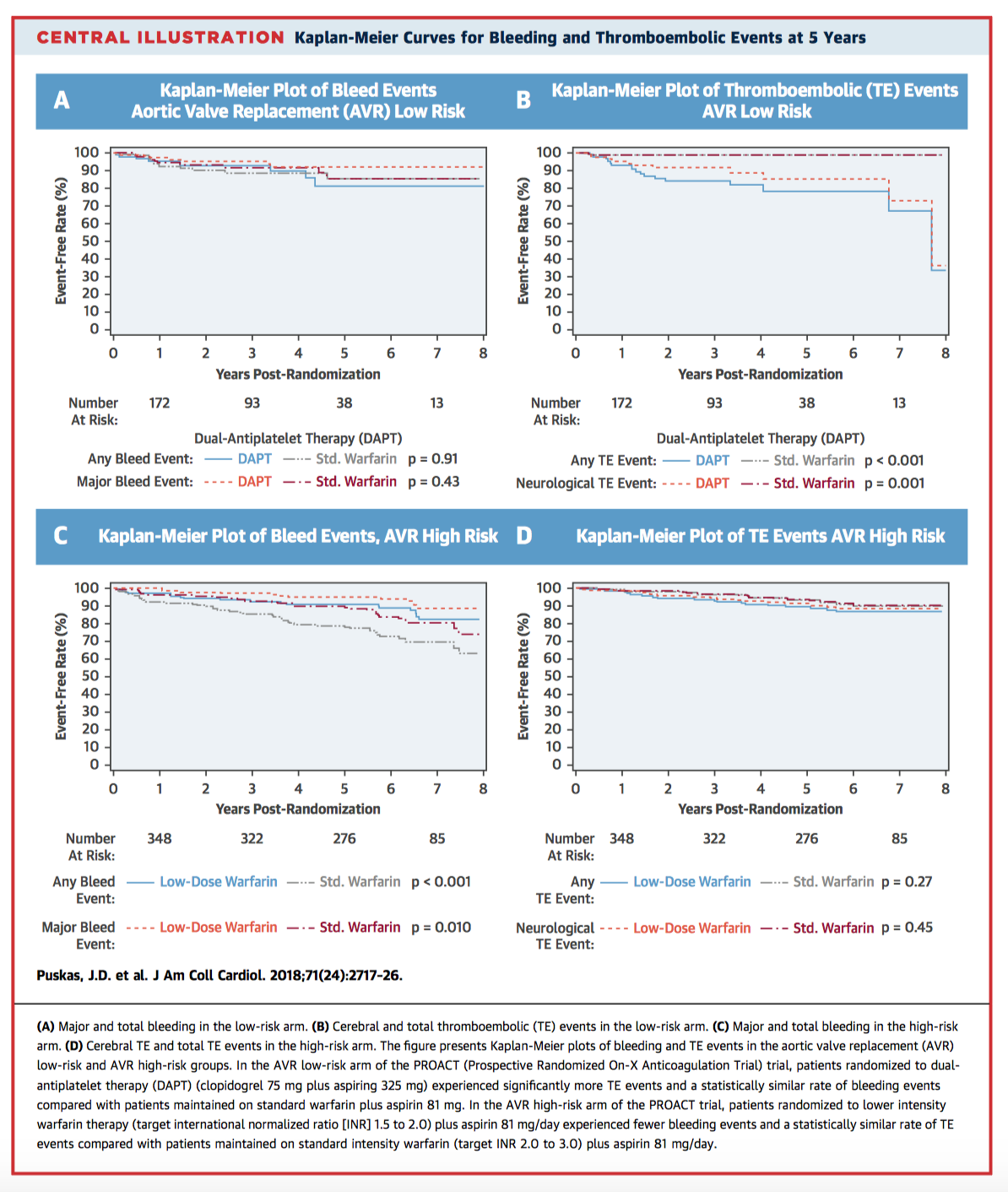
The burden of oral anticoagulation is a limitation of mechanical valve prostheses. This multicentre non-inferiority trial of 201 patients undergoing mAVR were randomised to receive DAPT or warfarin plus aspirin. DAPT was associated with higher rates of thromboembolism and valve thrombosis compared with control in the low risk arm.
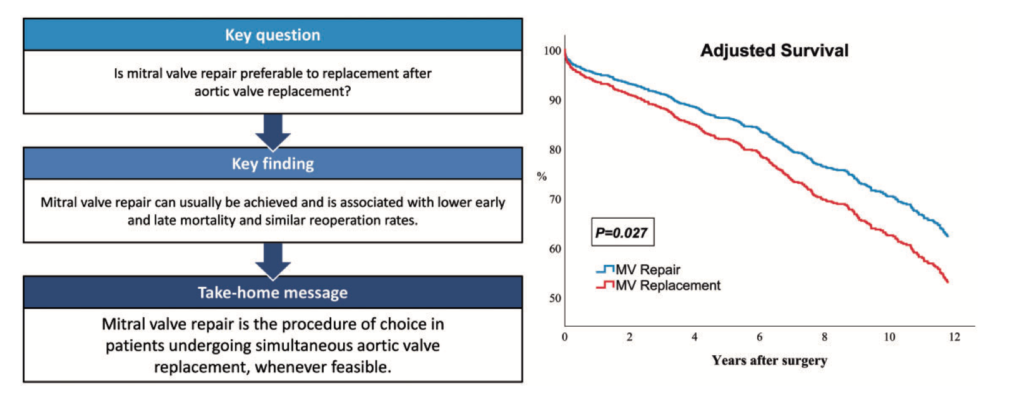
The reported superiority of mitral valve repair (MV) repair for isolated MV regurgitation has not been confirmed in mitro-aortic valve surgery. 1122 consecutive patients were submitted to concomitant and aortic valve surgery in two different centres. The authors concluded that MV repair can be performed in most patients undergoing aortic valve replacement, and should be the procedure of choice where possible given its favourable mortality rates and freedom from reoperation.
Whether the aortopathy associated with bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) disease occurs secondary to genetic or haemodynamic factors remains controversial. 406 patients underwent aortic valve and and ascending aortic replacement at a single institution. The authors concluded that mid-term imaging after AV and ascending aortic replacement indicated that if the aortic root was not dilated perioperatively, the risk of enlargement over time is minimal, negating the need for prophylactic root replacement in patients with BAV or TAV.
Summarised by Dr Sarah Catchpoole
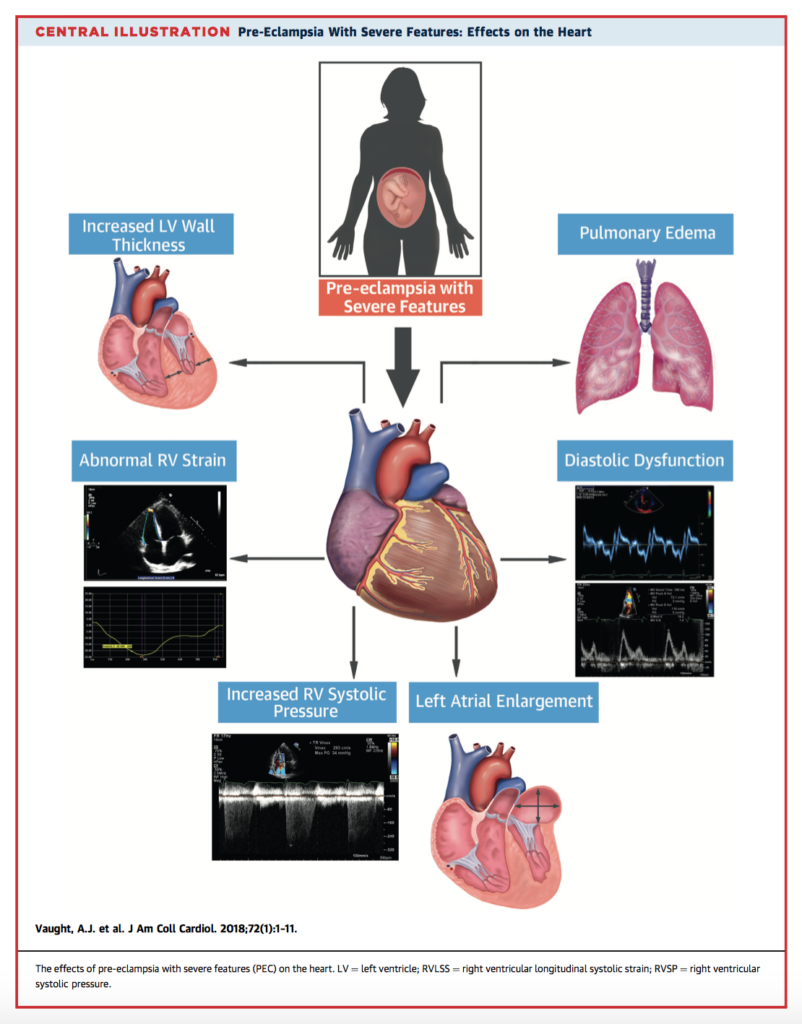
Vaught AJ, et al. Acute Cardiac Effects of Severe Pre-Eclampsia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Jul.
Pre-eclampsia affects 2—8% of all pregnancies and can have severe consequences including maternal end-organ damage and cardiac dysfunction. In this prospective observational cohort, transthoracic echocardiography was conducted on pregnant women <23 weeks gestation; 63 with severe preeclampsia (PEC), and 36 normotensive gestational-age matched controls. For right ventricular (RV) parameters, women with PEC had higher RV systolic pressures and diminished RV global longitudinal strain (p<0.001, for both). Left ventricular (LV) differences indicated abnormal cardiac remodelling (increased left atrial size, LV wall thickness, and mitral valve velocities, p<0.001 for all). 8 women (12.7%) had grade II diastolic dysfunction. There were no adverse secondary clinical outcomes in the control group, however 6 women with PEC (9.5%) had peripartum pulmonary oedema.
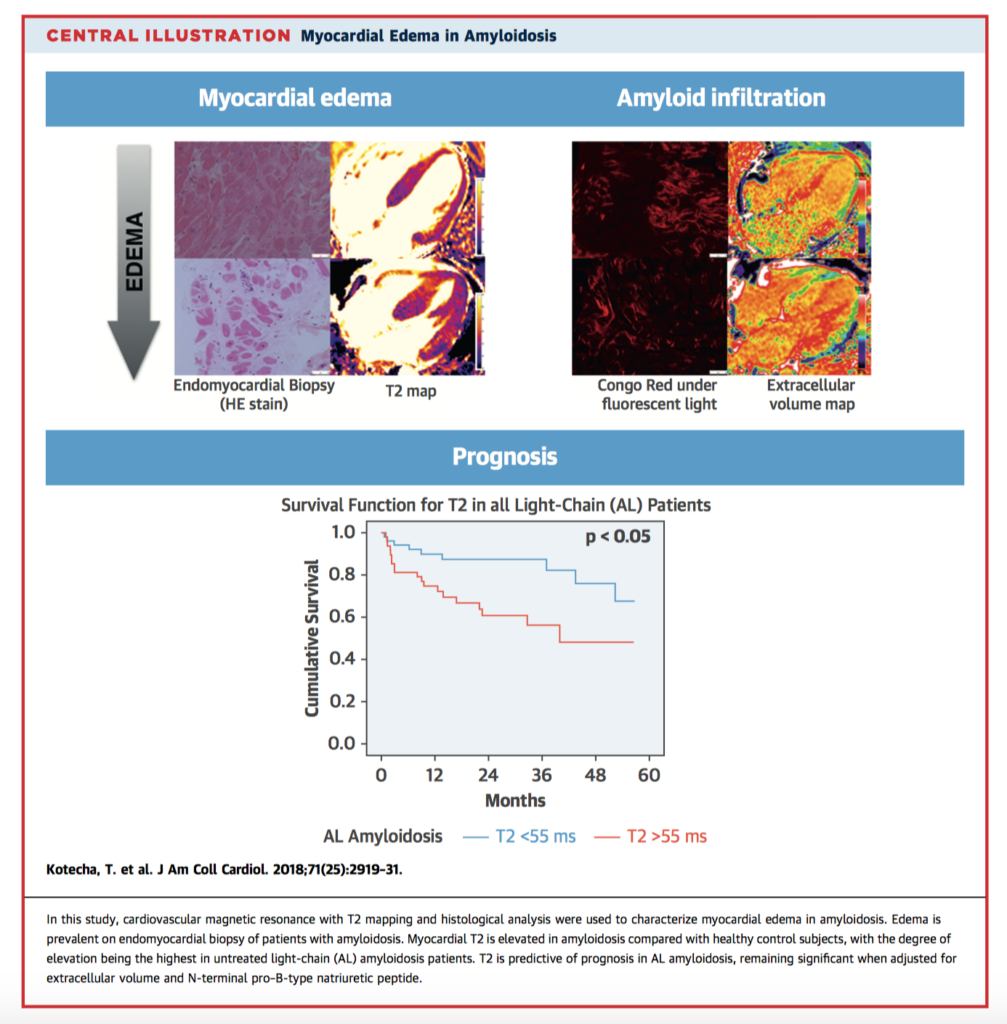
Kotecha T, et al. Myocardial Edema and Prognosis in Amyloidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Jun 26.
Cardiac involvement in amyloidosis is a major determinant of overall survival. Paradoxically however, while cardiac infiltration is greater in transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis, outcomes are worse in light-chain (AL) amyloidosis. The findings of this study suggest myocardial oedema as a possible additional mechanism or indicator of other mediating pathology. A total of 286 patients (including 163 with biopsy-proven ATTR or AL amyloidosis, 11 asymptomatic patients with ATTR genes, and 30 healthy controls) underwent cardiac MRI and were followed up for a mean 22.8±14.7 months). T2 signal was increased for all patients with amyloidosis, and highest for those with untreated AL amyloidosis. T2 also predicted death for patients with AL amyloidosis (Figure 3) even after adjusting for extracellular volume fraction and NT-proBNP (hazard ratio 1.32, 95% CI 1.05-1.67).
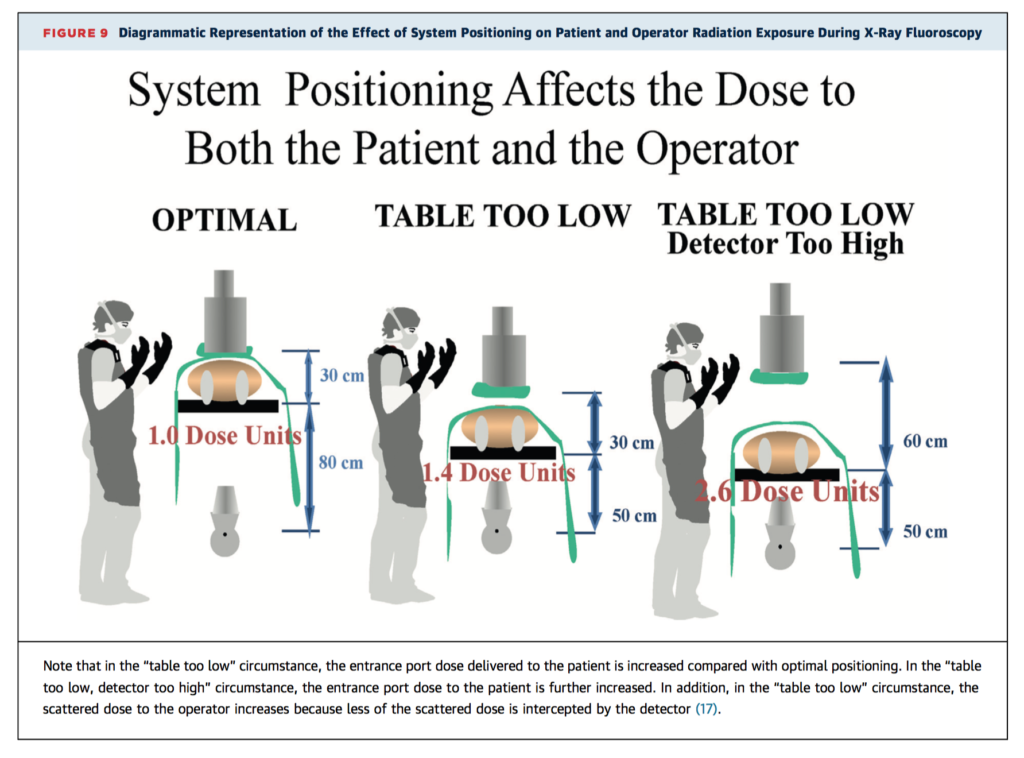
Part 1: Radiation Physics and Radiation Biology
Best Practices for Safety and Effectiveness
This three part new expert consensus document should be noted by all clinicians working with radiation. The parts (hyperlinks below) are clearly written, illustrated, and organised by numbered subsections for easy reference.
Summarised by Dr Andrew Haymet
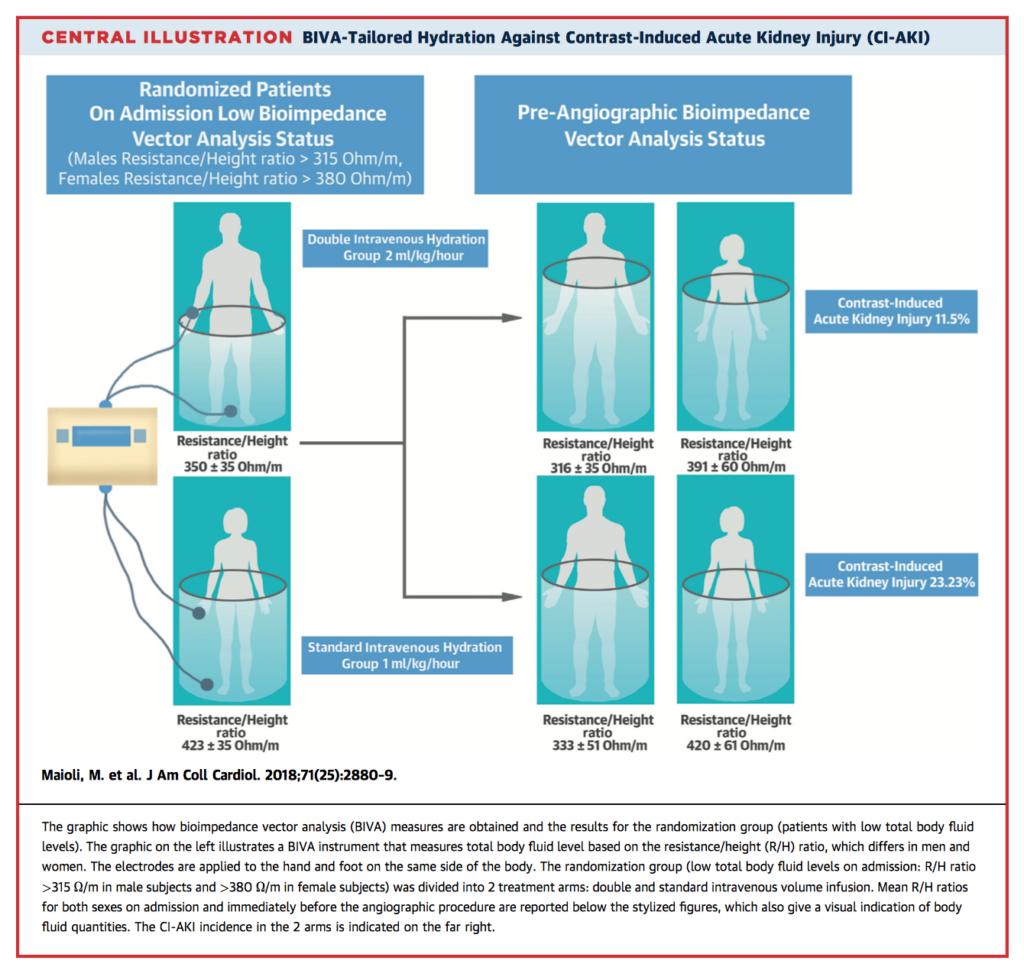
Intravascular volume expansion plays a major role in the prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI). This study of 303 patients aimed to compare the effect of standard and double intravenous (IV) infusion volumes in patients with low body fluid level, assessed by using bioimpedance vector analysis (BIVA), on the incidence of CIAKI after elective coronary angiographic procedures. The incidence of CI-AKI was significantly lower (11.5% vs. 22.3%; p = 0.015) in patients receiving double volume saline than in those receiving standard volume saline, respectively. The authors concluded that evaluation of BIVA levels on admission in patients with stable coronary artery disease allows adjustment of intravascular volume expansion, resulting in lower CI-AKI occurrence after angiographic procedures.
Although off label use of recombinant activated factor VII against refractory bleeding is incorporated in current guideline recommendations, safety concerns persist with respect to thromboembolic complications. 1180 patients in whom refractory bleeding developed despite substitution with specific haemostatic compounds (n = 167) received a single shot of very low-dose recombinant activated factor VII (20 mg/kg). Mortality, risk of thromboembolic complications, and freedom from stroke and acute myocardial infarction were analysed. The authors concluded that when combined with early and specific restoration of haemostatic reserves after cardiac surgery, very low-dose recombinant activated factor VII treatment of refractory bleeding is effective and not associated with any apparent increase in adverse events.
This prospective, randomised, double blinded, controlled study of 40 patients aimed to compare the effects of dobutamine and nitroglycerin to milrinone in young patients with severe pulmonary hypertension undergoing mitral valve replacement. Patients received either dobutamine and nitroglycerin (group 1) or milrinone (group 2). There was a more significant decrease in mean pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, and central venous pressure in group II than group I at all time points after cardiopulmonary bypass. The authors concluded that milrinone provides adequate cardiac performance, causing a greater reduction in pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure.