Welcome to the monthly SHDA Research Update. Our specialists have selected 3 seminal papers that have been recently published in each speciality.
Quick Links
Perioperative Medicine
Summarised by Sarah Catchpoole
The thin leaflets and anterior orientation of the pulmonary valve (PV) with respect to the oesophagus can make TEE evaluation challenging. The authors present a technique using 3D matrix array TEE simultaneous orthogonal plane imaging to view both the short and long axis of the PV. In 100 consecutive patients undergoing intraoperative TEE, all 3 leaflets were visualized in 65%, and 2 leaflets in 32%.
This expert review provides an overview of management options for incidental aortic stenosis (AS) found on intraoperative TEE during CABG, including conversion to an on-pump procedure, considerations for simultaneous or delayed valve replacement, and the role that the perioperative echocardiographic imaging plays in decision making.
In this first reported case series of paravertebral blockade in transapical TAVR patients, the authors retrospectively compared 48 patients receiving left sided single injections using 0.2% ropivicaine with supplemental clonidine to 13 controls. Intra-operatively, all patients received general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation. There were no complications from paravertebral anaesthesia, and patients had slightly lower intra-operative opioid administration (p = .05), a higher rate of extubation in the operating room (p = 0.0107), and lower incidence of atrial fibrillation (p = 0.0048). There was no significant difference in intensive care stay and 30-day mortality. The authors suggest paravertebral single shot blocks are safe and may have benefit for this high-risk patient population, but more prospective studies are required.
Cardiac Imaging
Summarised by Sarah Catchpoole
Obase et al. used 3D TEE to compare chordal length (CL), LV size, and leaflet surface area (LSA) in normal controls (n = 20) and patients with primary (degenerative) (n = 27) and secondary (degenerative) (n = 25) mitral regurgitation (MR). While there was no correlation in all three groups between CL and LV parameters, CL was elongated only in patients with primary MR and correlated with both LSA and mitral annular perimeter. In secondary MR, CL retained normal length despite LSA and LV enlargement. These findings have potential clinical implications for optimizing strategies for mitral repair surgery.
An overview of current, new and emerging imaging techniques for aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation. The authors recommend current clinical practice should include 3D echocardiography, dobutamine stress echocardiography, and multi-detector computed tomography to rule out measurement errors with 2D TTE and to confirm stenosis severity. However, cardiac magnetic resonance and PET-CT, while promising, require further research.
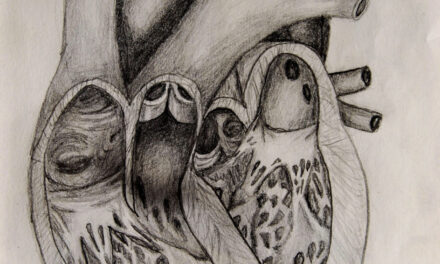
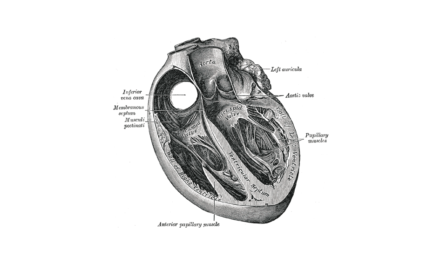
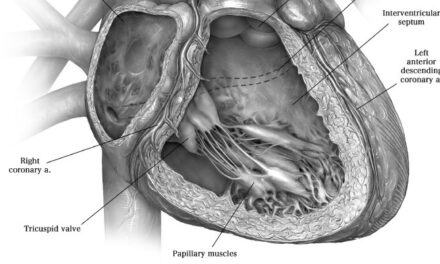
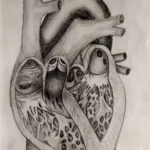
Typically, only two out of three leaflets are seen on standard 2D TTE of the tricuspid valve (TV) and it is hard to be sure which leaflets are being imaged. Using information from 3D multi-planar reconstruction in 106 patients, Addetia et al. defined six nonstandard 2D views tailored to depict specific leaflet combinations on the basis of anatomic clues and landmarks. When these six views were prospectively tested in an additional 54 patients, the agreement of TV leaflet identification against 3D MPR was excellent (k = 0.88, k = 0.93, and k = 0.98).
Cardiology
Summarised by Sarah Catchpoole
Reduced aortic valve leaflet motion preceding a stroke in a clinical trial patient who underwent TAVR prompted analysis of all patients in the clinical trial and in two registries. Reduced leaflet motion was found on four-dimensional, volume-rendered CT in 40% patients in the trial and in 13% in registries, noted in both transcatheter and surgical bioprostheses. While there was no significant difference in the incidence of stroke or TIA between patients with reduced and normal leaflet motion in the clinical trial (p=0.16), in the pooled registries, a significant difference was detected (p=0.007). Anticoagulation with warfarin but not dual antiplatelet therapy was associated with a decreased incidence of reduced leaflet motion. Therefore, reduced aortic valve leaflet motion in transcatheter or surgical bioprostheses is indicative of thrombus with potential to cause stroke, however this can be detected by CT and resolved by therapeutic anticoagulation with warfarin.
An animated video summary of valve leaflet motion is available on the NEJM website.
In 489 extreme-risk TAVR patients the rate of all-cause 2 year mortality was 36.6%, predicted by the presence of coronary artery disease, admission from an assisted living centre, and a STS score >15%. Haemodynamic outcomes were good, with 94% of patients in NYHA functional class I or II. 4.4% had moderate or severe paravalvular regurgitation. The authors conclude the presence of comorbid conditions rather than valve performance affected 2-year outcomes in these patients. These encouraging findings suggest improved access to TAVR could be provided to high risk patient populations, with conservative management more limited to patients with palliative conditions.
In a new systematic review and meta-analysis of causes of death following TAVR, the authors identified 28 studies for inclusion with a range of follow-up from 6 months to 3.8±2 years. Within 30 days of TAVR, the top three causes of mortality were infection/ sepsis (18.5%), heart failure (14.7%), and multiorgan failure (13.2%). Beyond 30 days, this changed to infection/sepsis (14.3%), heart failure (14.1%), and sudden death (10.8%). The authors note many of these causes are potentially preventable, with specific mention made to infection prophylaxis and heart failure optimisation.
Cardiothoracic Surgery
Summarised by Andrew Haymet
Remote ischaemic preconditioning (transient ischaemia and reperfusion of the arm) has been shown to improve biomarkers of ischaemia & reperfusion injury in cardiac surgery patients. Hausenloy et al. randomised on-pump CABG patients to either remote ischaemic conditioning group (four 5-minute inflations and deflations of the upper arm with a standard blood pressure cuff) or a sham conditioning (control) group. Conditioning was found to have no significant effect on 12-month combined primary end points (death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, or stroke).
Alternative exposure techniques are becoming increasingly warranted in mitral valve surgery, especially as the complexity of cardiovascular patient presentations continue to increase. This paper describes methods of transventricular and transaortic mitral valve repair, and discusses their advantages. These approaches are safe and efficient, particularly in cases where a left ventriculotomy is required, or in cases of aortic valve endocarditis with involvement of the mitral valve.
Reproducibility is an important component of aortic valve-sparing reimplantation and annuloplasty. 58 fresh human aortic valves were dissected, and the topographic relationships between the ventriculoaortic junction (VAJ), basal ring (BR) and sinotubular junction (STJ) were analyzed. The external height of the non/left commissure was found to be greater than the other two commissures. This is significant for aortic annuloplasty techniques, because incomplete proximal root dissection will impede placement of the device down to the aortic root level.