Welcome to the monthly SHDA Research Update. Our specialists have selected 3 seminal papers that have been recently published in each speciality (Cardiology, Cardiac Surgery, Cardiac Imaging, Perioperative Medicine).
Cardiology
Summarised by Sarah Catchpoole
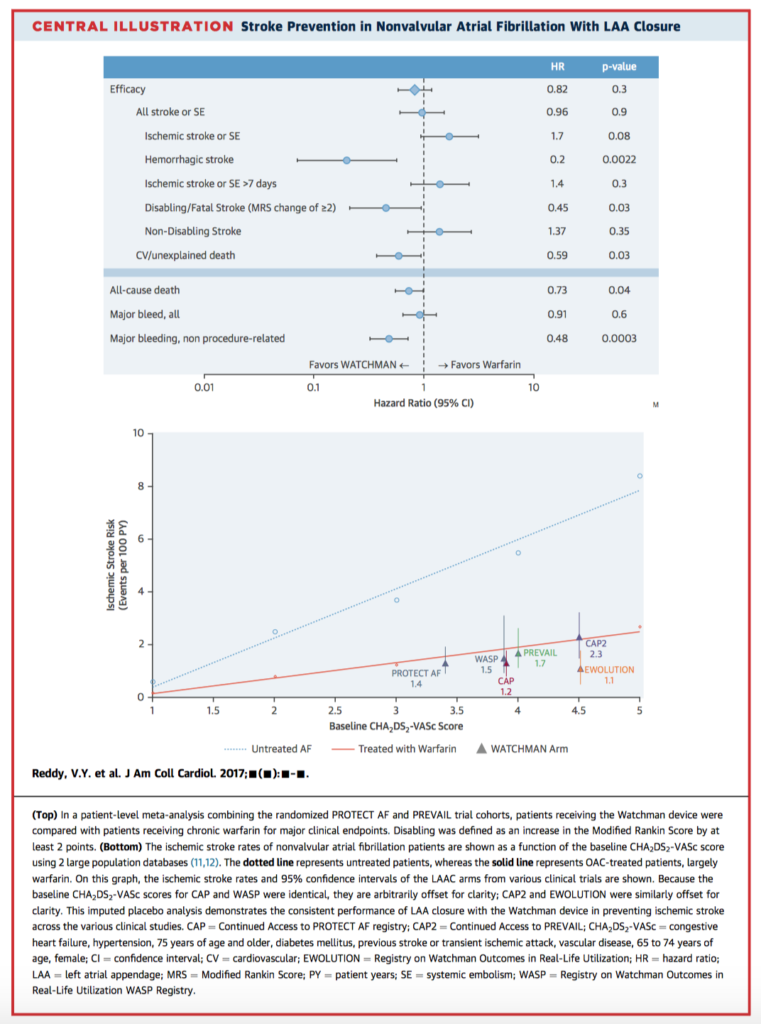
This paper presents the five year outcomes of the PREVAIL trial, both alone and in combined meta-analysis with the PROTECT AF trial. Both clinical trials compared the Watchman left atrial appendage closure (LACC) device to standard oral anticoagulation with warfarin (2:1 randomisation) for prevention of stroke in non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF), with slightly different inclusion criteria. The combined results, including 1114 patients over 4343 patient-years, revealed no significant difference between groups for the composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism (SE), or cardiovascular/unexplained death (hazard ratio 0.820, p=0.27). In addition, the LACC group was associated with improved rates of haemorrhagic stroke, disabling/fatal stroke, cardiovascular/unexplained death, all-cause death, post-procedure bleeding, and overall with higher freedom from all-cause death (hazard ratio 0.73; p < 0.04). The authors conclude that LACC is effective for stroke prevention compared to anticoagulation with warfarin, and provides further benefits, especially reduction of haemorrhagic stroke and overall mortality.
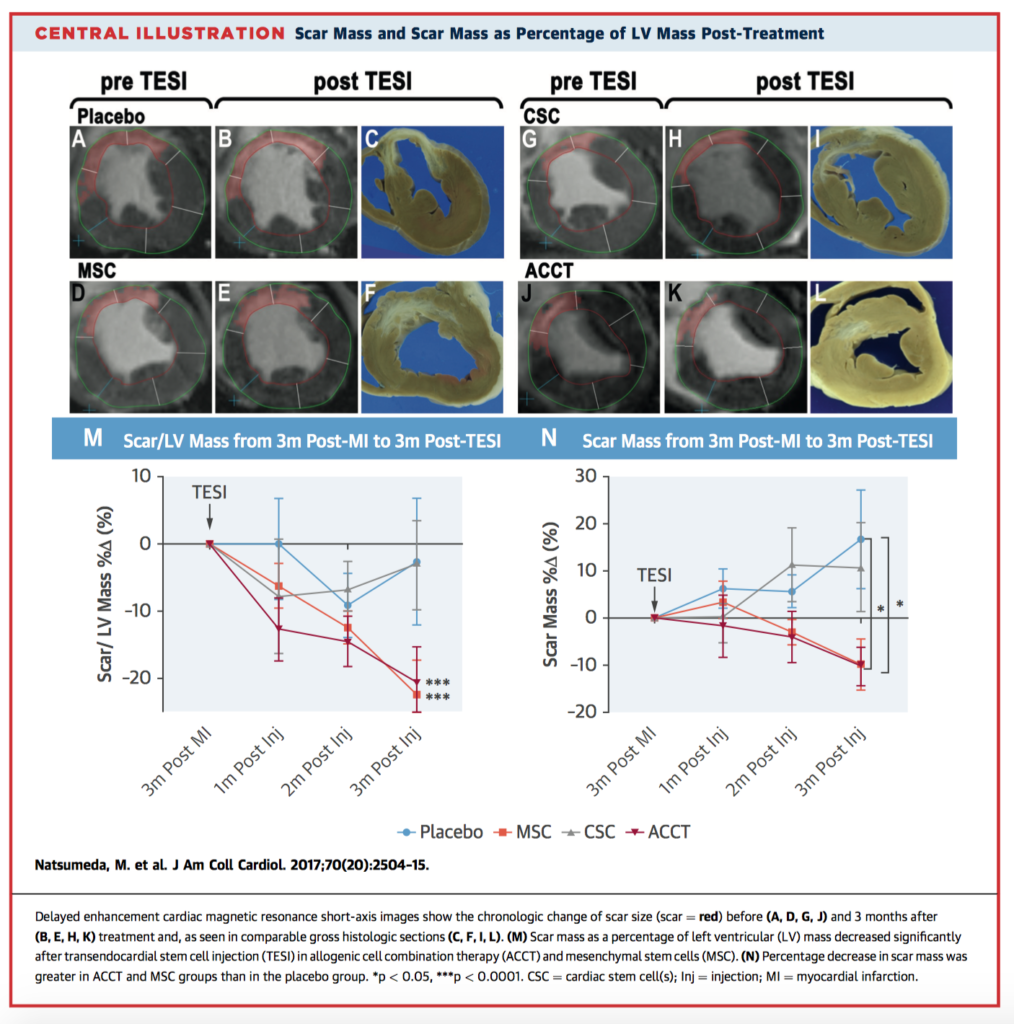
Natsumeda et al. have demonstrated enhanced cardiac regeneration and left ventricular functional recovery in the hearts of Göttingen swine with ischemic cardiomyopathy given transendocardial injections of stem cells. Using a blinded, placebo-controlled design, both allogeneic cell combination therapy (ACCT) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) were able to significantly reduce scar size. However only ACCT was able to suppress progressive negative remodelling by preventing increases in chamber volumes, and furthermore was associated with increased cardiomyocytes, noncardiomyocytes, and phospho-histone H3+ (a marker of mitosis) compared to placebo. There were no adverse immunogenic reactions up to 3 months post-administration. The authors suggest ACCT is a good candidate for further testing in human trials.
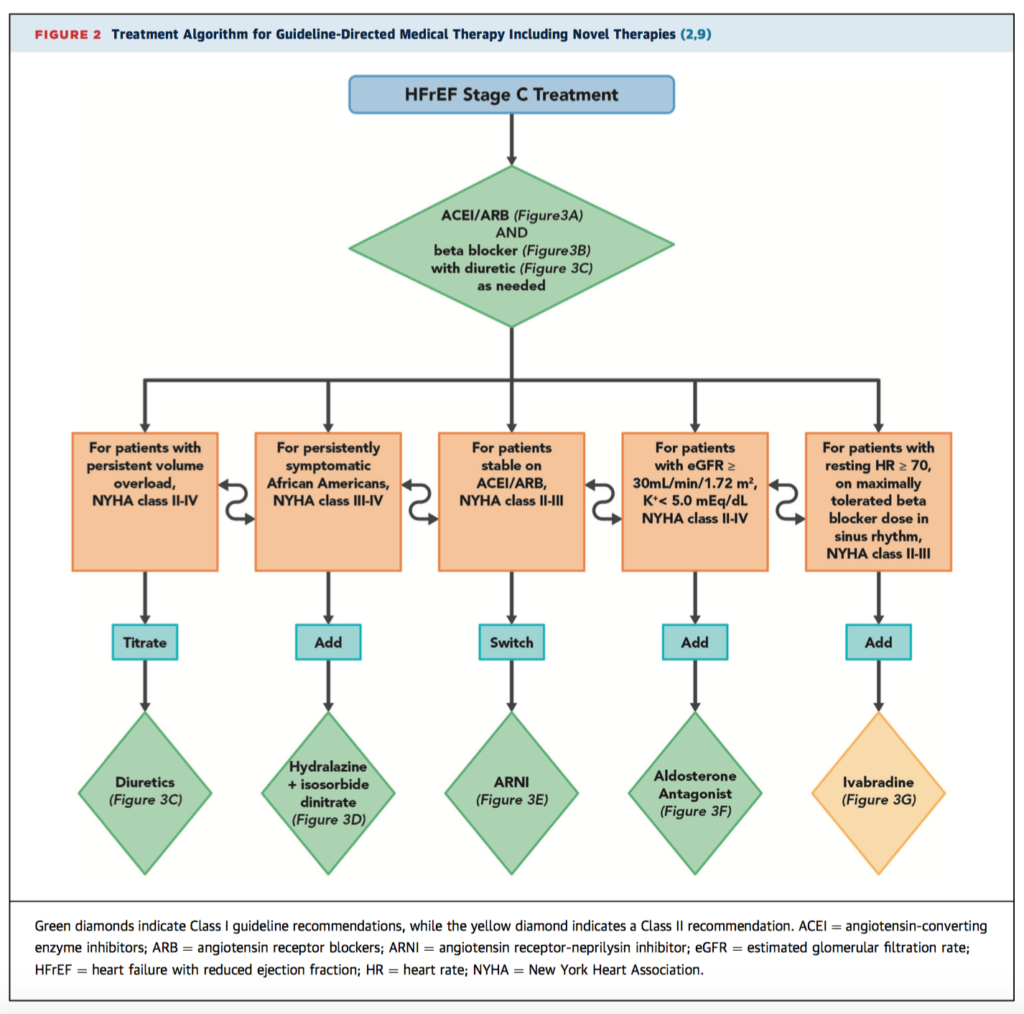
These new expert consensus guidelines from the ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of America aim to provide a definitive reference framework to assist with the increasingly complex management decisions for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The clinical algorithms are structured around 10 pivotal issues in the management of HFrEF that the authors identified, including medication regimes, when to refer to a heart failure specialist, management of common comorbidities, and palliative care considerations. Figure 2, below, provides one of the sample algorithms. While the authors stress no guideline supersedes clinical judgement, they hope to streamline care, improve outcomes, and assist in rational decision making, especially where clinical trial evidence is lacking.
Cardiac Surgery
Summarised by Andrew Haymet
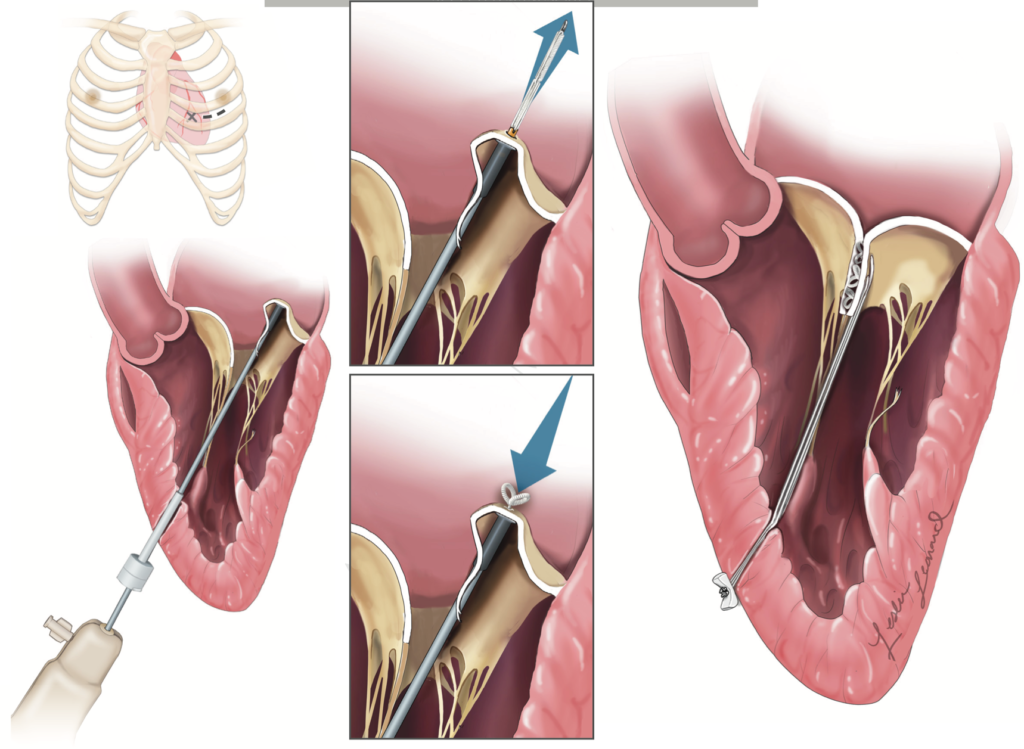
This prospective, multicentre study of 30 patients with severe degenerative mitral regurgitation (MR) evaluated the safety and performance of the Harpoon Mitral Valve Repair System (H-MVRS), a transoesophageal echocardiographic-guided device designed to implant artificial expanded polytetrafluorethylene (ePTFE) cords on mitral leaflets in the beating heart. The primary (30 day) endpoint was successful implantation of cords with MR reduction to moderate or less, which was achieved in 27/30 patients (90%). There were no deaths, strokes, or permanent pacemaker implantations. At one month, MR was mild or less in 89 % (24/27) and was moderate in 11%(3/27). At 6 months, MR was mild or less in 85 % (22/26), moderate in 8% (2/26), and severe in 8% (2/26). H-MVRS ePTFE cordal implantation can reduce the invasiveness and morbidity of conventional mitral valve surgery. The authors concluded that this device had a promising safety profile and that further prospective trials are warranted.
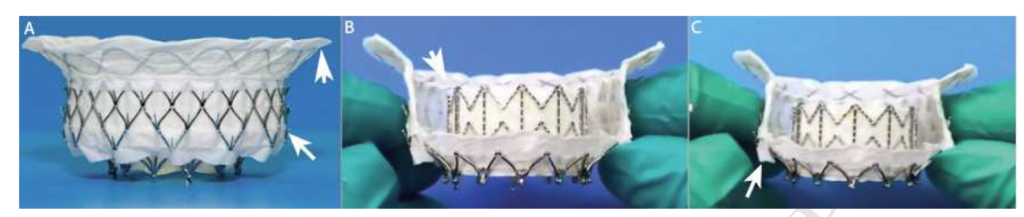
Transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) is a potential therapy for patients with symptomatic, severe mitral regurgitation (MR). The feasibility of this therapy remains to be defined. This multicentre study of 50 consecutively enrolled patient who underwent TMVR with new self-expanding valve system. Device implantation was successful in 48 patients with a median deployment time of 14 (IQR, 12, 17) minutes. The 30 day mortality was 14%, with no disabling strokes, or repeat interventions. Improvements in symptom class (79% in NYHA I or II at follow-up; p<0.0001 vs. baseline), and Minnesota heart failure questionnaire scores (56.2 ± 26.8 vs. 31.7 ± 22.1; p=0.011) were observed. The authors concluded that TMVR with the valve was feasible in a population at high-or extreme-risk for conventional mitral valve replacement. These results inform trial design of TMVR in lower-risk patients with severe mitral valve regurgitation.
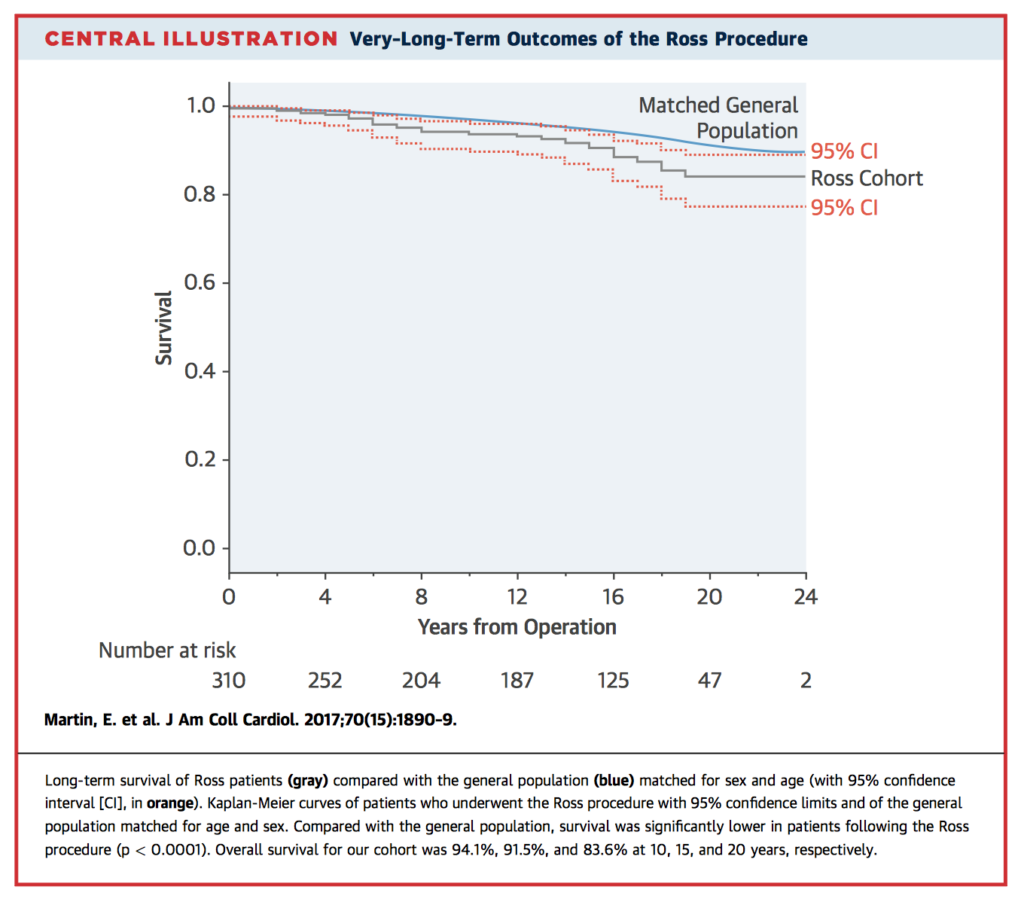
This single institution study reviewed the outcomes of 310 patients who underwent the Ross procedure between January 1990 and December 2014 (mean age 40.8 years). Bicuspid aortic valve was diagnosed in 227 patients (73.2%), and the most common indication for surgery was aortic stenosis (n = 225 [72.6%]). Freedom from any Ross-related reintervention was 92.9% and 70.1% at 10 and 20 years, respectively. There were 4 hospital deaths (1.3%), and overall survival at 10 and 20 years was 94.1% and 83.6%, respectively. Compared with the general population, survival was significantly lower in patients following the Ross procedure when matched on age and sex (p<0.0001). The authors concluded that the Ross procedure was associated with excellent long term valvular outcomes and survival, however unlike previous reports, long term survival was lower in Ross patients compared with matched subjects. Adults presenting with aortic insufficiency or a dilated aortic annulus or ascending aorta were at higher risk of reintervention.
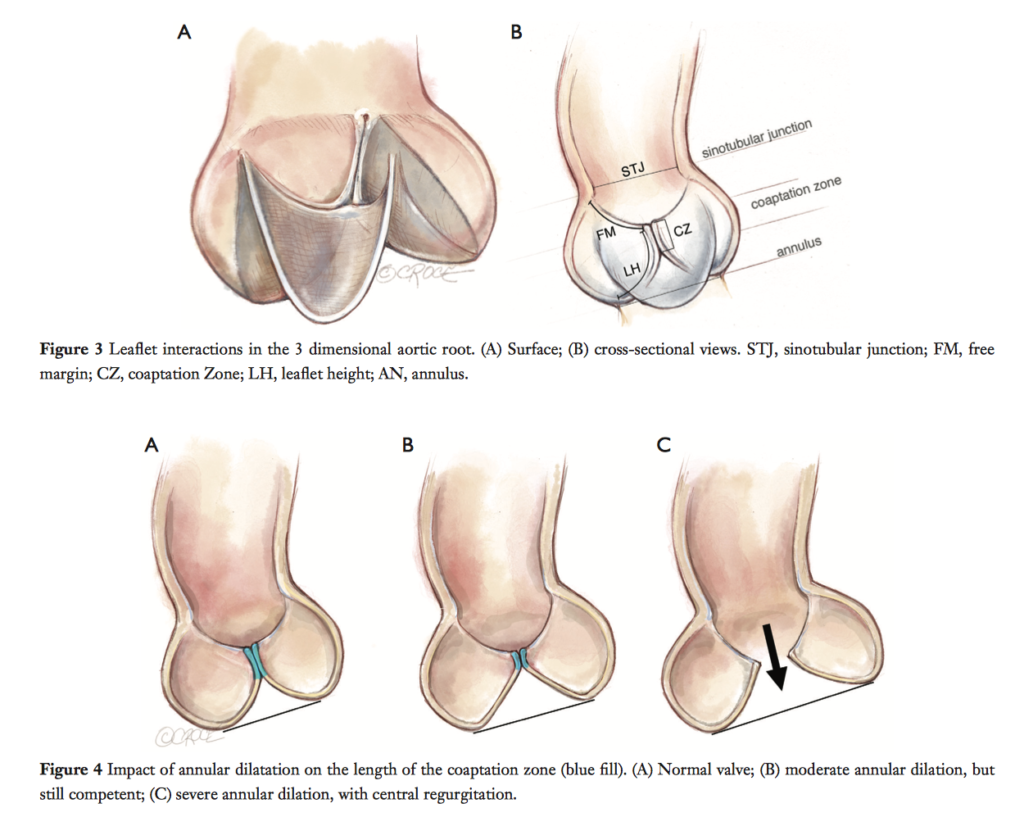
Aortic valve sparing root surgery (AVSRS) is a safe and durable alternative for patients with dilated roots or pure aortic regurgitation (AR), which avoids the risks of anticoagulation or valvular degeneration with prosthetic valves. Notwithstanding the theoretical challenges of greater tissue fragility in Marfan syndrome (MFS), AVSRS has been demonstrated to have equal outcomes in this condition as it does in those without MFS. This operative technique paper clarifies the the complex structure-function relationships of the aortic valve, and describes specific technical details of established techniques found to be successful in preserving long term valvular function postoperatively.
Cardiac Imaging
Summarised by Sarah Catchpoole
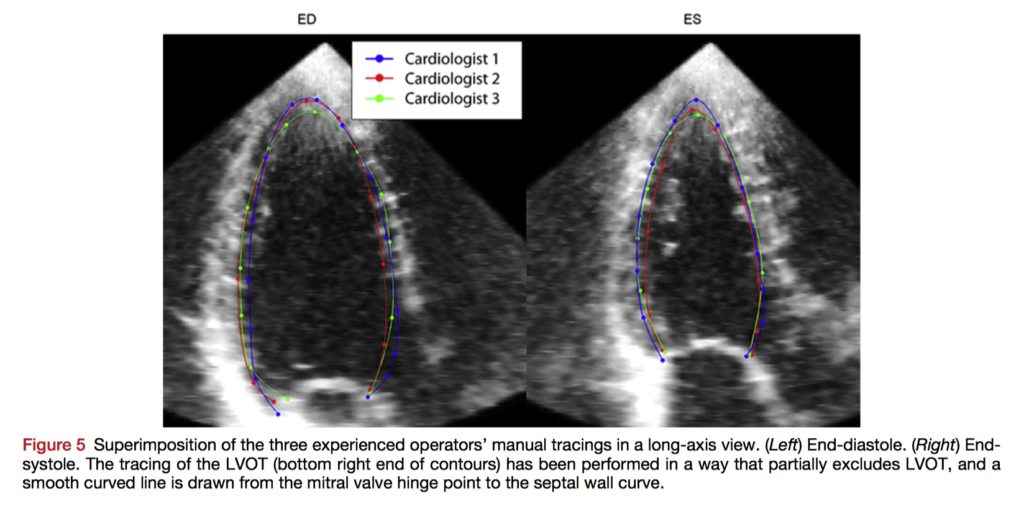
There is no established standard guideline or procedure available for 3D echocardiography (3DE) endocardial border tracing, and no studies directly comparing tracings between operators. Papachristidis et al. analysed the performance of three expert operators using 45 standard 3D LV echocardiographic data sets, tracing according to a protocol. There was excellent agreement among the experts; intraclass correlation coefficients for end-diastolic volume, end-systolic volume and ejection fraction were all >0.93, while absolute distances between tracings were 1.11±0.45 mm. The areas of highest distance error were the apical cap, anterior and anterolateral walls, and basal anteroseptum. When novice operators traced reference meshes, they were more accurate if they followed the tracing protocol. The authors conclude their protocol produces accurate tracings with small interobserver variability, and that they have identified key areas more prone to tracing error.
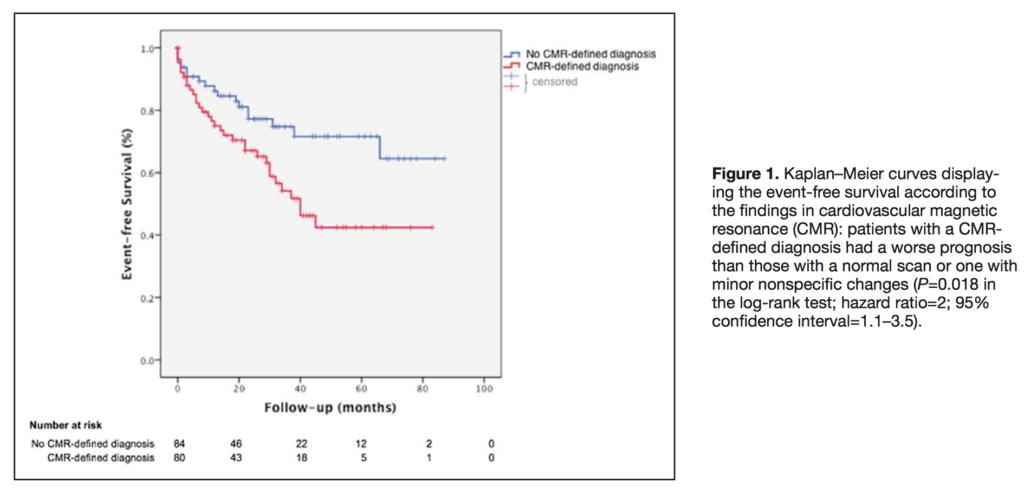
This retrospective, blinded study shows that the addition of cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging to a clinical pathway for investigation of the cause of sudden cardiac arrest contributes to the diagnosis in up to half of all patients. In 164 patients without coronary artery disease, CMR was decisive in the diagnosis of 50 cases (30%) and contributed to the diagnosis of 80 cases (49%). The most common final diagnoses were idiopathic (36%), arrhythmic (14%), dilated cardiomyopathy (13%), myocarditis/sarcoidosis (13%), occult ischaemic heart disease (7%), and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (5%). Patients were then followed up over a median period of 32 months. A CMR defined diagnosis was associated with a higher rate of major adverse cardiac events, with late gadolinium enhancement, left ventricular ejection fraction, and especially right ventricular ejection fraction predictive of future events.
Those with non MRI-conditional pacemakers or defibrillators (“legacy” devices) are often unable to undergo clinically indicated MRI scans due to safety concerns. In this prospective study, the authors performed 2103 MRI scans on 1509 patients with legacy devices using a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla. Their safety protocol included disabling tachyarrhythmia functions, asynchronous mode for the pacing-dependent, or demand mode for other patients. There was only one case of device programming failure (pacemaker with <1 month battery life), which subsequently required replacement. Transient power-on reset occurred for eight patients (0.5%). After a median follow up of 1 year with data available for 63% of patients, there were no long-term clinically significant adverse events or changes in lead parameters.
Perioperative Medicine
Summarised by Andrew Haymet
This special article is a fourfould research review of selected highlights of 2017 in cardiothoracic and vascular anaesthesia. Firstly, transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) offers signicant potential to treat patients at prohibitive surgical risk, with potential use in intermediate or even low risk patients in the future pending further experience and improvement in safety profile. Secondly, with respect to coronary artery disease, bioresorbable coronary stents likely require prolonged DAPT due to a higher thrombotic risk. The roles of cardiopulmonary bypass and BIMA grafts in CABG should be individualized, taking into account the clinical presentation and the latest evidence. Thirdly, Levosimendan does not improve major clinical outcomes after adult cardiac surgery associated with heart failure either as rescue or prophylactic therapy. Centrifugal-flow LVADs have further improved clinical outcomes in the setting of these devices for surgical management of end-stage heart failure. Finally, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ (STS) updated 2017 guideline strongly recommends surgical ablation for AF at the time of concomitant mitral surgery (class I recommendation, level A evidence). Furthermore, surgical ablation for AF should also be considered in appropriate patients at the time of concomitant isolated aortic valve replacement, isolated coronary artery bypass graft surgery, and aortic valve replacement plus CABG surgery (class I recommendation, level B evidence).
This single centre, prospective, single blind study of 97 patients undergoing elective valve surgery aimed to compare the effect of dexmedetomidine combined with isoflurane versus isoflurane anaesthesia on brain injury after cardiac surgery. Jugular blood samples were drawn for analysis of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) levels on time points of: T1 (before induction); T2 (5 minutes after cardiopulmonary bypass [CPB] onset); T3 (after CPB off); T4 (postop day 1); T5 (postop day 2). In both groups, serum MMP-9 and GFAP concentrations increased after CPB, with the peak values occurring after CPB. MMP-9 concentrations in the Dex-Iso group were lower than the Iso group at T3 and T4. GFAP concentrations in the Dex-Iso group were lower at T3 but were higher than the Iso group at T2. The authors concluded that the use of dexmedetomidine decreased the biochemical markers of brain injury but did not improve the neuropsychological test result after cardiac surgery.
This prospective randomized controlled study aimed to assess the feasibility, safety and potential useful effect of adenosine as a postconditioning agent in 60 patients undergoing CABG. Compared with the control group, ejection fraction, fractional shortening, cardiac index (2.9 +/- 0.3 v 2.2+/-0.3 L/min/m2, p=0.032 at 60 min post bypass) and diastolic function indices were significantly better in the adenosine postconditioning group at most time points in the postbypass period. The authors concluded that adenosine postconditioning provided cardiac protection, as reflected by favourable systolic and diastolic function indices, less cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase-MB release, lower incidence of arrhythmia and use of inotropes, and shorter duration of postoperative mechanical ventilation and ICU stay.